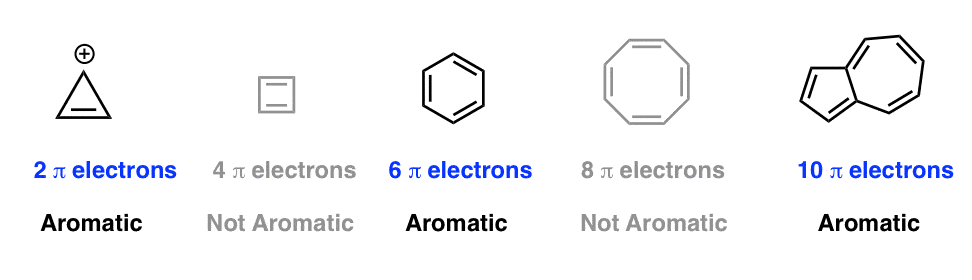
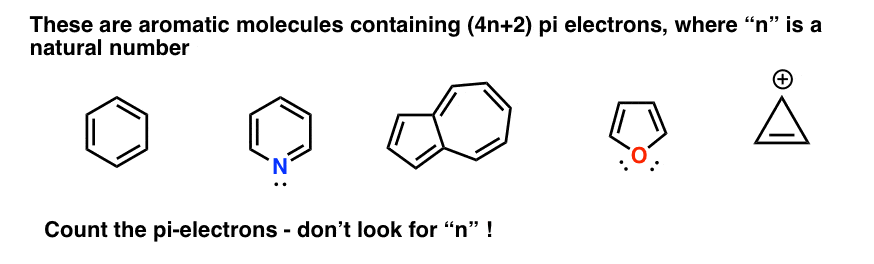
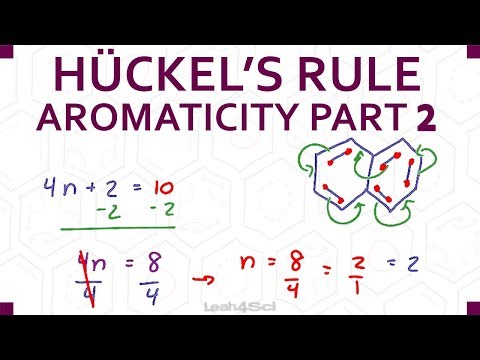
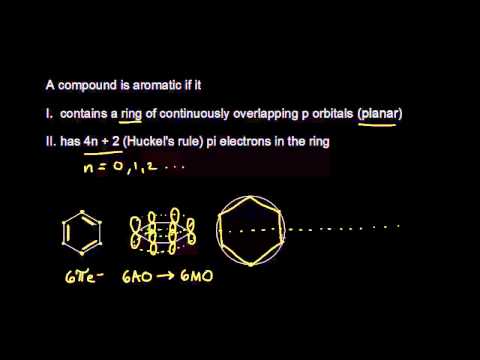
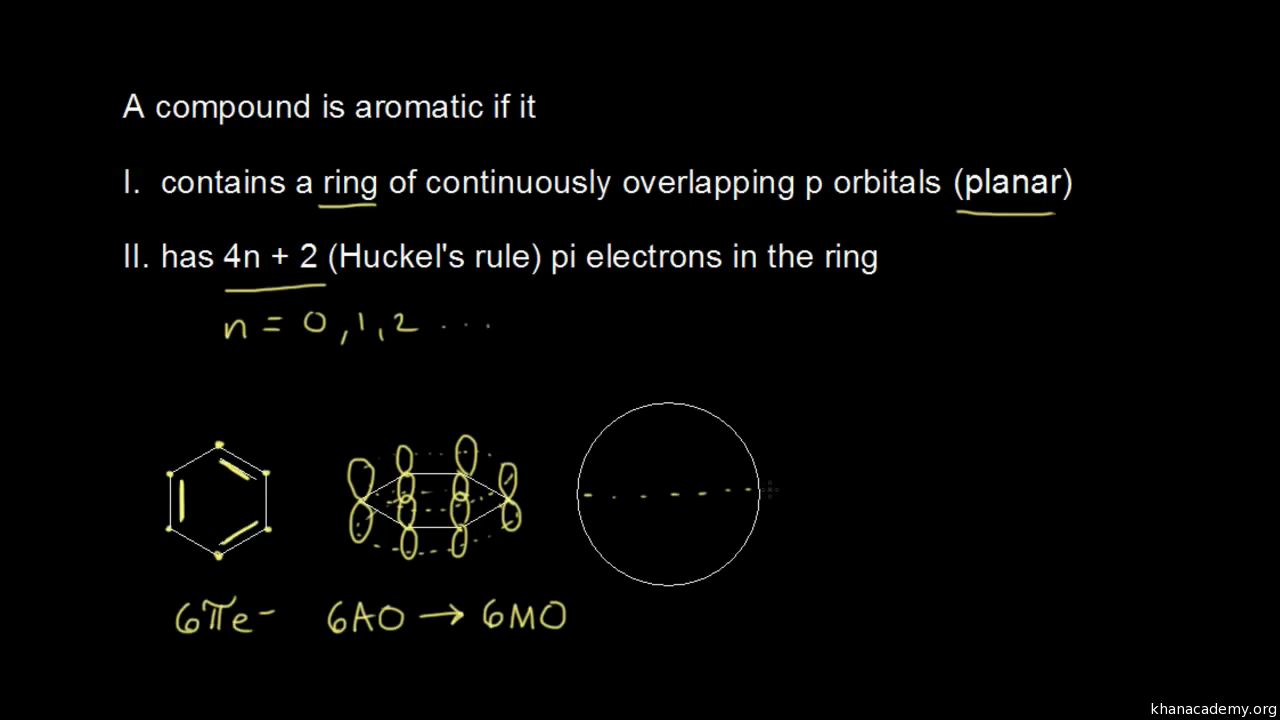
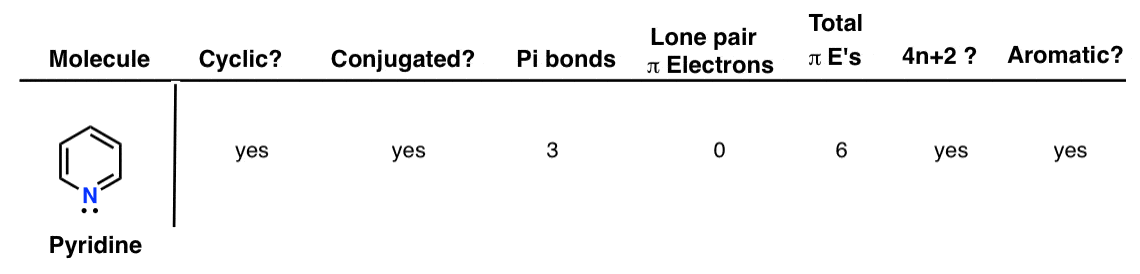
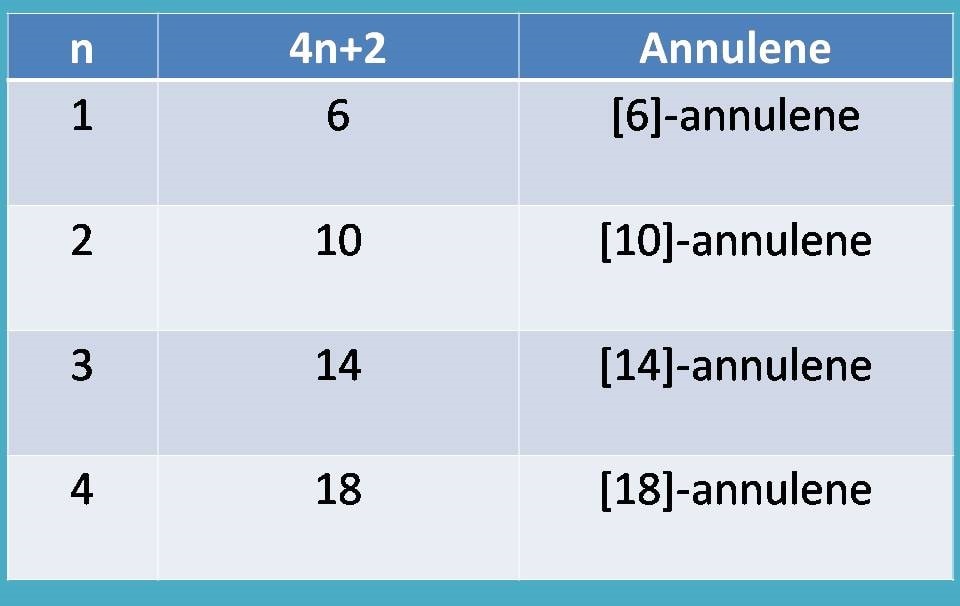
4n+2 Pi Electrons
For n = 1, we calculate that a ring of six carbon atoms should be aromatic.

4n+2 pi electrons. The correct answer is (8) Annulene. Thermal rearrangements of all conjugated systems containing 4n + 2 pi electron are stereospecific. 3) There should be 4n+2 pi electrons in inside the ring where n can be any whole number.
I, II, and III D. HÜCKEL'S RULE So, imidazole has two π electrons from the left and right double bonds each. Heilbronner predicted that large annulenes incorporating a 180 ° twist of the pi-electron band would be destabilized in the 4n+2 electron case, but stabilized if occupied by 4n electrons.
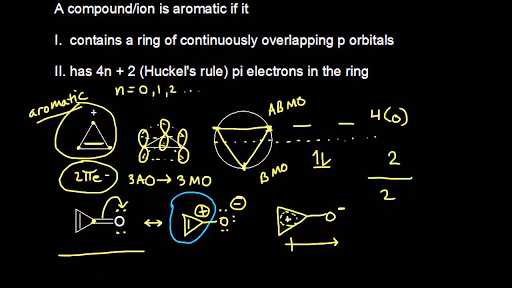
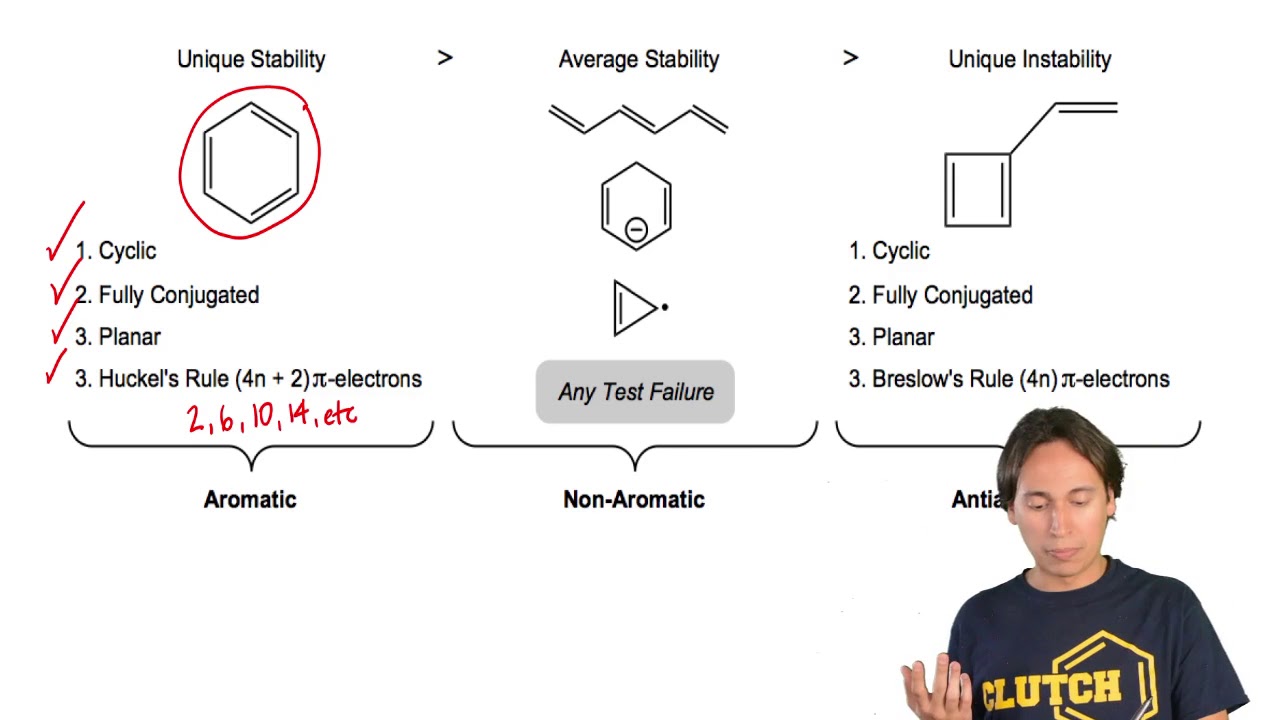
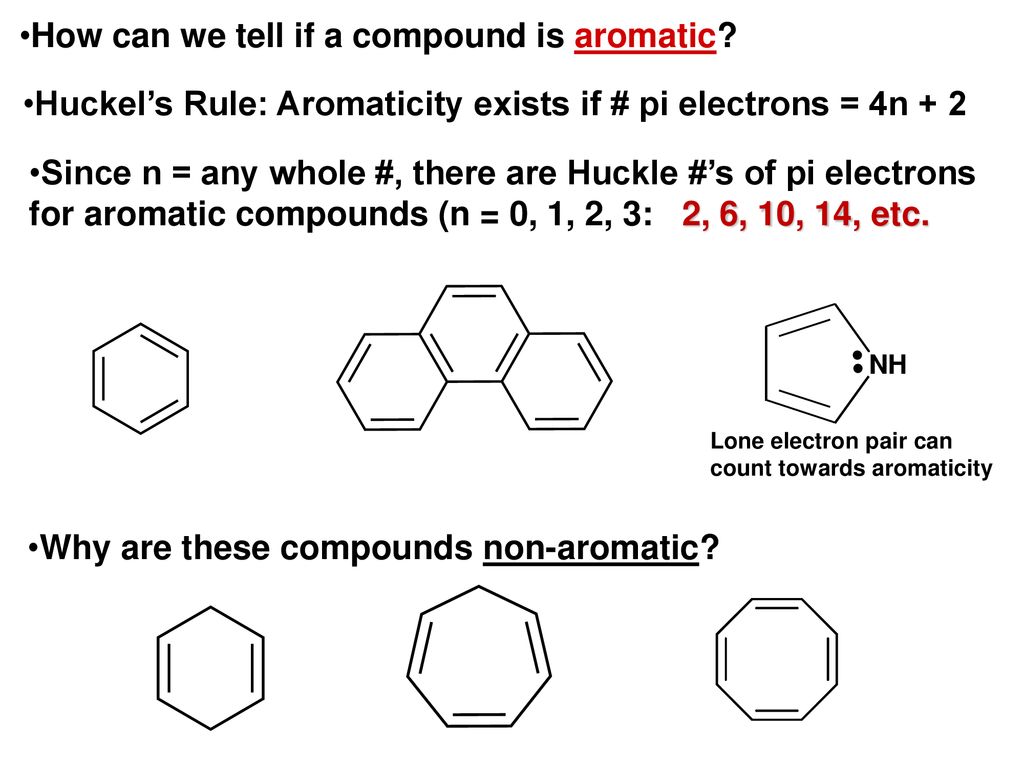
This is based on preservation of orbital symmetry in the highest occupied molecular orbital. The lone pair of electrons assumes a sp2 hybridized orbital, making the molecule planar, adding 2 more electrons to the ring to give 4n+2 pi-electrons and creating the 5th pi orbital necessary to complete Huckel’s Rule and results in an aromatic ion. If the total number of electrons available for pi bonding fits the formula 4n+2 where n is an integer (thus the number is 2, 6, 10, 14, etc.) in a cyclic system, the system will be aromatic, which means those electrons will be delocalized throughout the system.
Planar, in an SP2 hybridized orbital, over every atom of the ring;. Simply put, Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that a monocyclic system will be aromatic if there are 4n + 2 delocalised electrons, (n an integer) contained within it. Therefore, 4n + 2 = 6 and n = 1, and it follows Hückel's Rule.
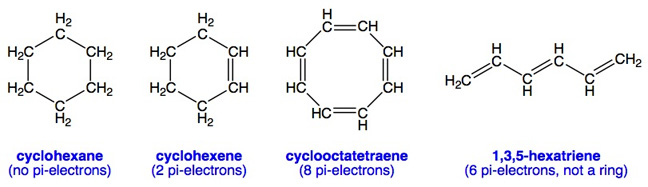
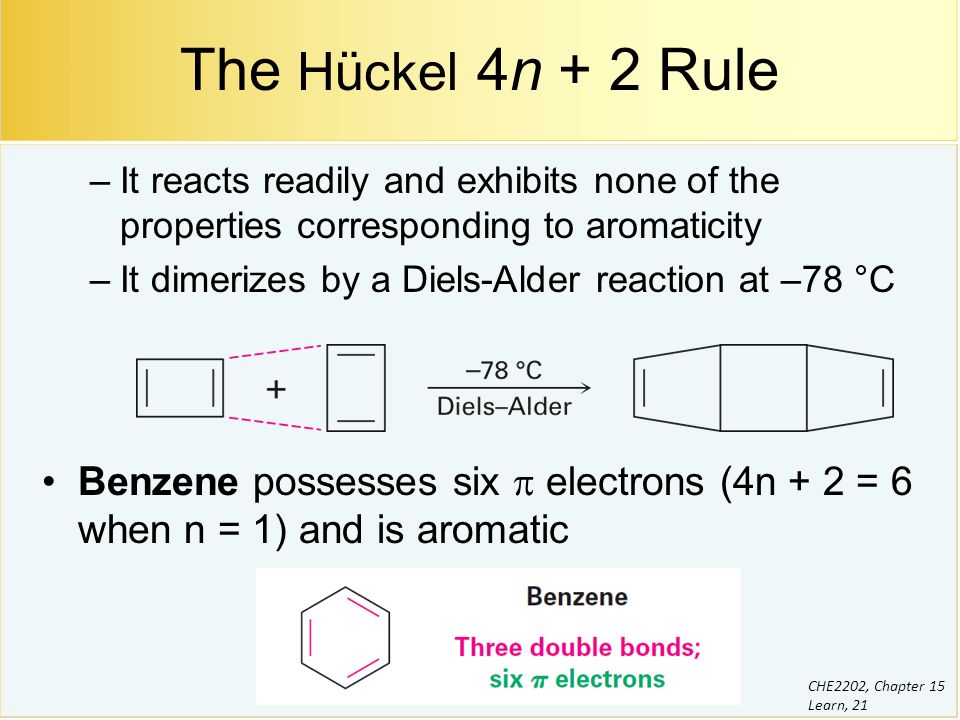
Benzene has 6 pi-electrons and (4× 1)+2 = 6, thus it obeys Huckel’s Rule while cyclooctatetraene has 8 pi-electrons 4n+2 ≠ 8, thus it does not follow Huckel’s Rule. According to Huckle's rule, there are four basic conditions to be a aromatic compounds, which are as follows - Compound must be cyclic. The Huckel 4n + 2 Pi Electron Rule A ring-shaped cyclic molecule is said to follow the Huckel rule when the total number of pi electrons belonging to the molecule can be equated to the formula ‘4n + 2’ where n can be any integer with a positive value (including zero).
If the ring contains 4n + 2 pi electrons, the molecule should be aromatic. Each atom in the. I and IV C.
Another example is formation of a carbocation, a common intermediate in substitution and. Yep - you only count the pi electrons in the ring (6). N=1 if aromatic should have 6 pi electrons n=2 if aromatic should have 10 pi electrons.
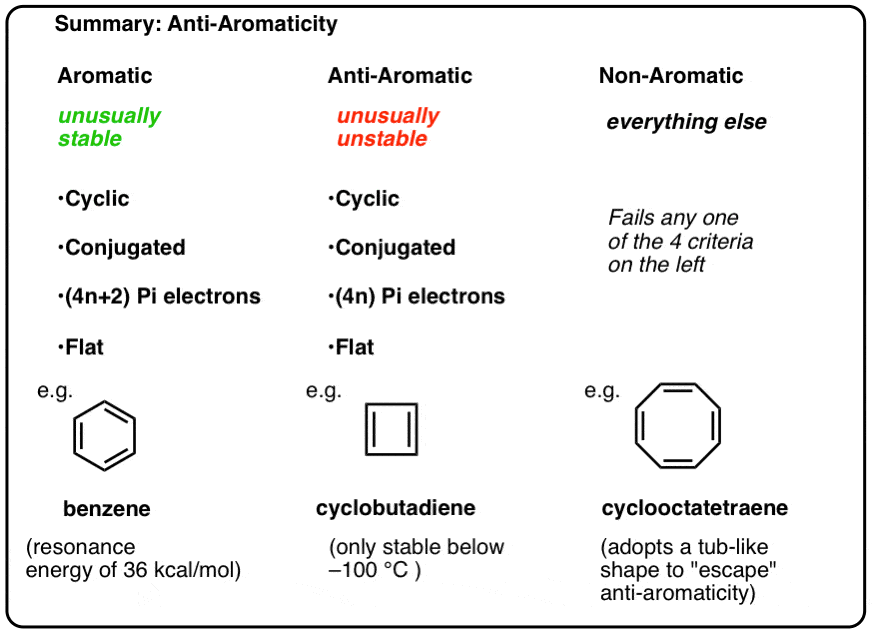
This is an antiaromatic ion. So, benzene is aromatic and cyclooctatetraene is a non-aromatic compound. Unlike aromatic compounds, which follow Hückel's rule (4n+2 π electrons) and are highly stable, antiaromatic compounds are highly unstable and highly reactive.
But Hückel’s law does not require an electronically neutral structure. Rocketbooster, I know the recent mcat question to which you refer in your post. Consider a few ring sizes that fill the bill.
A cyclic ring molecule follows Huckel's rule when the number of its pi electrons equals 4n+2 where n is zero or any positive interger (although clearcut examples are really only established for. This rule would come to be known as Hückel's Rule. Those electrons form three conjugated double bonds.
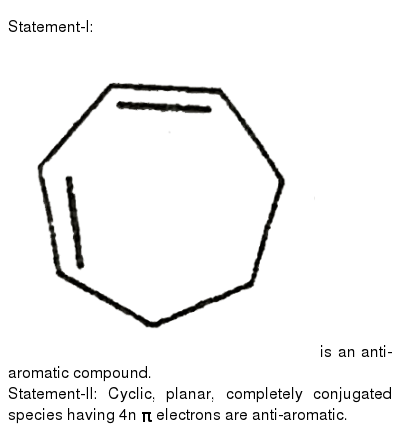
Hückel’s Rule dictates a flat ring with 4n + 2 π (pi) conjugated electrons. N can be any non-negative whole number, including zero. If the number of pi electrons is 4n instead of 4n +2 with above rules, than it confers that the molecule is anti-aromatic.
Criterion of possessing 4n + 2 pi electrons;. All compounds must obey Huckel’s Rule i.e. Benzene To aid in counting the electrons the following factors may help:.
-for some reason none of my organic chemistry textbooks, lectures, etc explain what N actually is, so I made this video. The 3 C=C in benzene mean that we have 3 pairs of π electrons = 6 π electrons = a 4n+2 number where n=1. The huckel rule just says (it was discovered empirically, later confirmed by calculations ) that all systems with 4n+2 pi-electrons (6, 10, etc) are extremely stable and do nor behave like normal.
In benzene (which can be written in its Kekulé form of three single and three double bonds, cyclohexatriene) there are 6 pi-electrons (i.e 4n+2 where n=1) so it is aromatic and planar with all bond angles being 1. Aromatic compounds need to have 4n+2 pi electrons in the ring system. To determine the number of pi electrons, determine the number of pi bonds and multiply by two.
Benzene matches the description. All the ring atoms must be carbons. Benzene has 6 pi electrons (n = 1) so it is aromatic.
Each atom in the cyclic, conjugated system must contribute a p orbital to the π system. Note that "n" in Huckel's Rule just refers to any whole number, and 4n+2 should result in the number of pi electrons an aromatic compound should have. $\begingroup$ Huckel's rule demands that there be 4n+2 pi electrons in the ring.
The Huckel anti-aromaticity rules are:. This is because all aromatic compounds must follow Huckel's Rule, which is 4n+2. I and II B.
Another way to put the 4n+2 rule is that if you set 4n+2 equal to the number of electrons in the pi bond and solve for n, you will find that n will be a whole number. It has six carbon atoms and six pi electrons. Aromatic molecules contain ___ pi electrons.
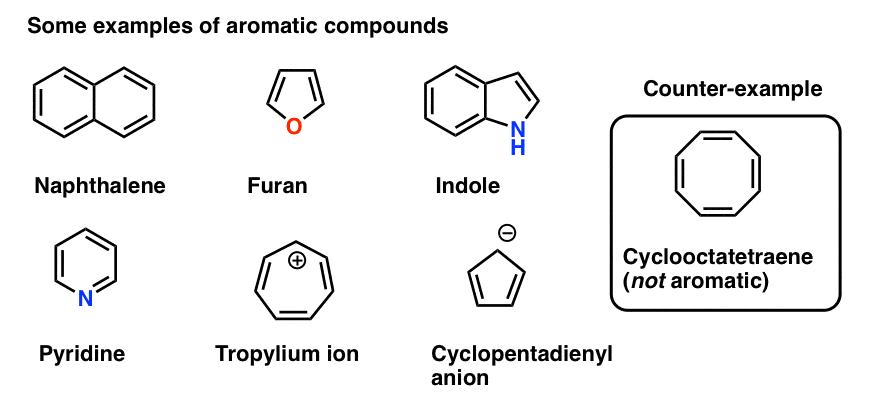
In order to be aromatic the system also has to be flat, conjugates and cyclic, and all the atoms need to be sp2 hybridized to be characterized as aromatic. 6 = 4n + 2, so n=1 and thus aniline is aromatic. Heterocyclic aromatic anions with 4n + 2 .pi.-electrons.
Ignore the sigma bonding electrons and look at the electrons available for pi bonding. And if the above rules are not satisfied, than the compound is non-aromatic. To be aromatic, there have to be (4n+2) pi-electrons in a planar delocalised cyclic system (where n is a positive integer).
Huckel arrived at this rule by performing molecular orbital calculations on cyclic systems containing x carbon atoms, and with each carbon atom supplying one pi electron. The molecule must have 4n + 2 electrons in a conjugated system of p orbitals (usually on sp 2-hybridized atoms, but sometimes sp-hybridized);. Have a closed loop of 4n+2 pi-bond electrons, where n is equal to any integer (0,1,2,3,…) However, anti-aromatic compounds have an unusual INSTABILITY to them.
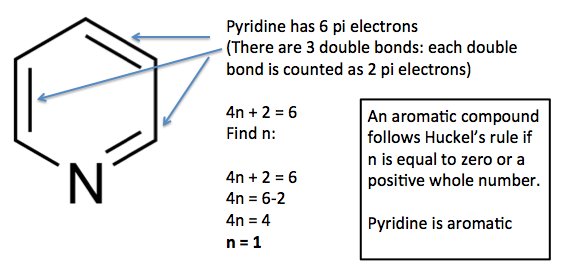
His rule states that if a cyclic, planar molecule has 4n+2 π electrons, it is considered aromatic. His rule states that if a cyclic, planar molecule has 4n+2 π electrons, it is considered aromatic. Also, as it turns out, the lone pair on the bottom nitrogen IS within the ring, making it 6 electrons.
It is benzene (C₆H₆). Only one of the lone pairs is actually in a pure 2p orbital perpendicular to the ring, which means those count as pi electrons. Show transcribed image text.
Basically it states that if a compound possesses 4n+2 pi electrons (where n can be an integer greater than or equal to zero--i.e., 0,1,2,), it is aromatic, PROVIDED that the compound is cyclic, planar, and has an unhybridized p orbital on every atom in the ring structure. The pi electron count is defined by the series of numbers generated from 4n+2 where n = zero or any positive integer (ie, n = 0, 1, 2, etc.). To avoid the instability of antiaromaticity.
Cyclooctatetraene is a non -aromatic compound and does not possess aromaticity. If the number of pi electrons is 4n instead of 4n +2 with above rul. That series of numbers pertains to a mathematical sequence 4n+2.
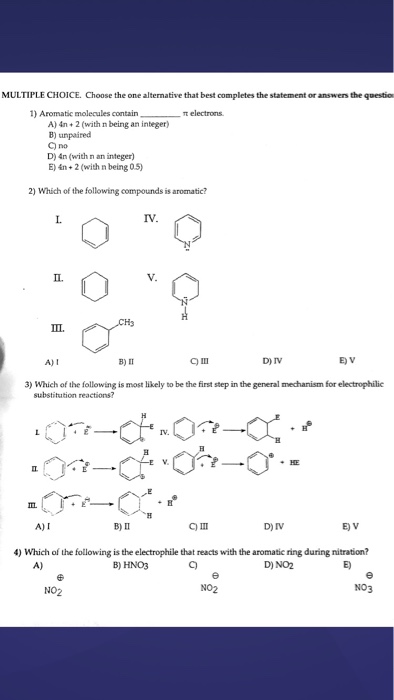
Have one pi orbital per atom of the ring;. -The condition that aromatic molecules must h ave 4n+2 pi (π) electrons is sometimes calle d “ Hu ckel’s rule ”. A) 4n + 2 (with n being an integer) B) unpaired C) no D) 4n (with n an integer) E) 4n + 2 (with n being 0.5) Which of the following compounds is aromatic?.
Therefore n must be a whole number that satisfies this equation 4n+2=x, where x = the number of electrons in the pi bonds. This rule would come to be known as Hückel's Rule. CHECK ALL That Apply* Total Of 4n+2 Pi Electrons, Where N Is A Whole Number Cyclic Planar Fully Conjugated Is This Compound Aromatic?.
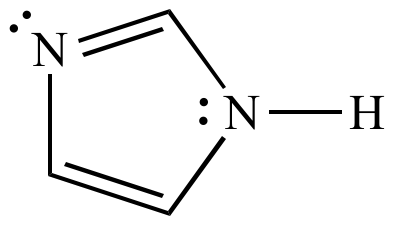
Compound must be conjugated. The most common case in six pi electrons (n = 1) which is found for example in benzene, pyrrole, furan, and pyridine. If the N is in the ring, then its lone pair will count towards the pi electrons used for Huckel's rule ONLY.
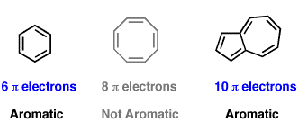
Similar annulenes having 4n pi-electrons have been termed "antiaromatic". Each carbon contributes one, making for a total of 5 from the carbons. Given the structures of aromatic molecules, the number of pi-electrons has to be 2, 6, 10, 14, 18, 22, etc.
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. This organic chemistry video tutorial shows you how to tell if a compound is aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic by using huckel's rule / number of 4n+2 pi. A system with delocalized pi electrons in a ring.
(4n+2) pi electrons in the ring. In 4n + 2, if we put n = any integer, then (4n) + 2 \\neq\ 8, thus it does not obey Huckel’s Rule. 3) There should be 4n+2 pi electrons in inside the ring where n can be any whole number.
Start studying OChem2- Exam 2. A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V Which of the following it most likely to be the first step in the general mechanism for electrophilic substitution. Compound must contain (4n+2)pi electrons, where n is any whole number.
The smallest neutral ring with these qualifications has n = 1. Among P, Q, R and S, the aromatic compounds(s) is/are (A) P (B) Q (C) R (D) S. The one on the right is fully conjugated and has a 4n+2 number of pi electrons (where n=0), so it’s aromatic.
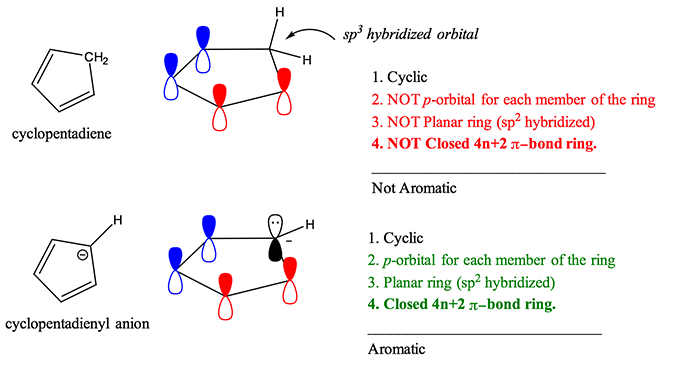
In order for pyrrole to have 6 pi electrons it needs to contribute the lone pair of electrons on its nitrogen to the aromatic ring system. For instance, benzene is a six carbon ring structure. Molecules must have 4n+2 pi-electrons.
Each carbon contributes one, making for a total of 5 from the carbons. The carbanion can resonate with the double bond, which means the molecule is fully conjugated. However, resonance stabilization rises to its highest level when not only are equivalent structures available, but the conjugated system is cyclic and has 4n+2 pi electrons in the cyclic system.
If a cyclic conjugated molecule follows this rule, it is an aromatic compound. I, III and IV. Want to see the full answer?.
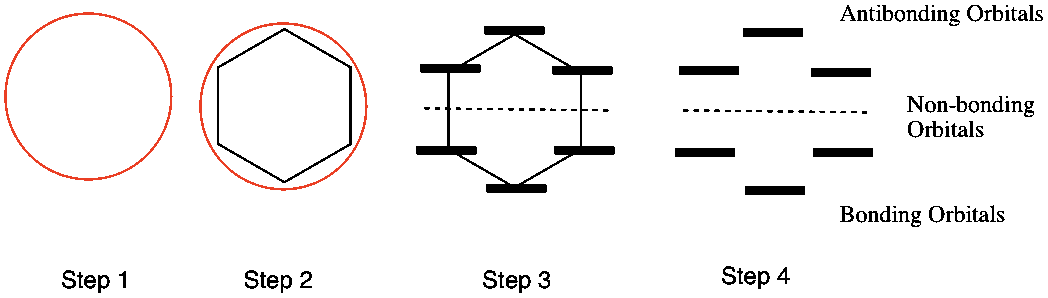
Hückel's 4n+2 rulen is equal to 0 or any integer. Systems containing 4n pi electrons show the opposite conrotatory mode. According to MO theory, the pi electrons of benzene occupy three molecular orbitals, y 1, y 2, and y 3, all of which are lower in energy than an electron in an isolated p orbital.The linear combination of p orbitals that generates y 1 extends over all six carbon nuclei.
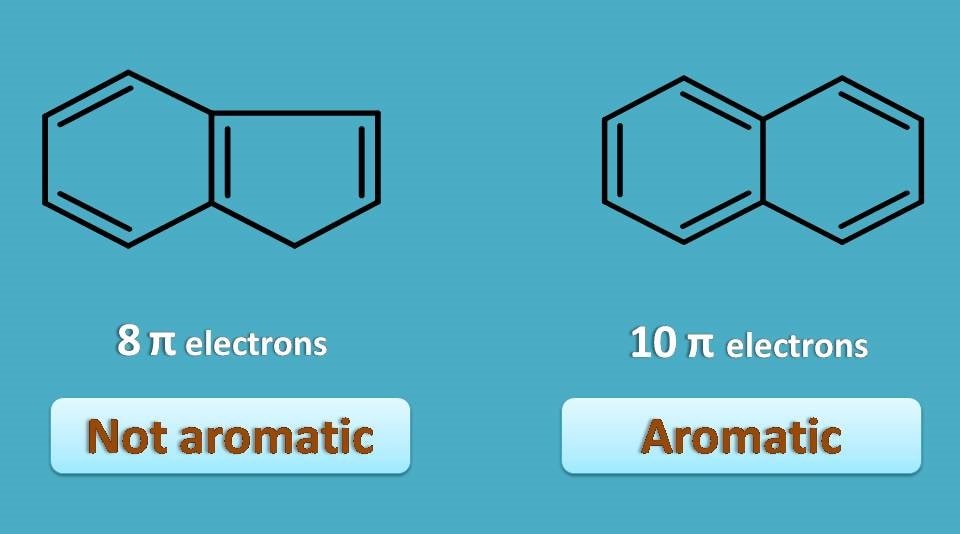
Check Answer and Solution for above question from Chemistry in Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Tardigrade. This question hasn't been answered yet Ask an expert. (image will be uploaded soon) (Number of pi- electrons = 8 as it has 4 pi- bonds, So, for any value of ‘n’, 4n+2 cannot be equal to 8.).
The one in the middle has a 4n number of pi electrons (where n=1), so it’s antiaromatic. 4n pi electrons in a ring. Huckel’s rule just states that the amount of pi electrons/pi system has to follow 4n+2 where n is a natural number.
Such cyclic, conjugated systems are sometimes referred to as aromatic. Without getting into specifics, in general I will say:. The two electrons that occupy y 1 experience the Coulombic attractions exerted by all six nuclei.
Q The 4n+2 Rule is also sometimes called the Huckel Rule. What is N in the 4n+2 rule?. Aromaticity , Antiaromaticity, Homoaromaticity and the Hückel (4n + 2) Rule.
2, 6, 10, 14 etc. In 1931, German chemist and physicist Erich Hückel proposed a theory to help determine if a planar ring molecule would have aromatic properties. In 1931, German chemist and physicist Erich Hückel proposed a theory to help determine if a planar ring molecule would have aromatic properties.
Aromatic, because 4n + 2 = 6 pi electrons in the ring (with n = 1), planar, fully conjugated all around, and cyclic.

Chemistry Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Rule In Order To Be Facebook

What Is The Difference Between Anti Aromatic And Non Aromatic Species Quora

Solved 12 The Number Of P Electrons Present In An Antiar Chegg Com
4n+2 Pi Electrons のギャラリー

13 6 Aromaticity Organic Chemistry Ii

Electrocyclic Reactions

Aromatic Compounds Overview Chemgapedia
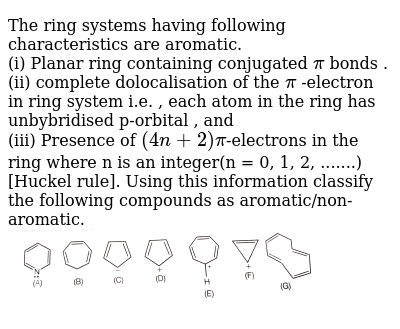
The Ring Systems Having Following Characteristics Are Aromatic B

Previous Page Next Page Page 5 Of 8 Question 4 Points Which One Of The Homeworklib
The Msds Hyperglossary Aromatic
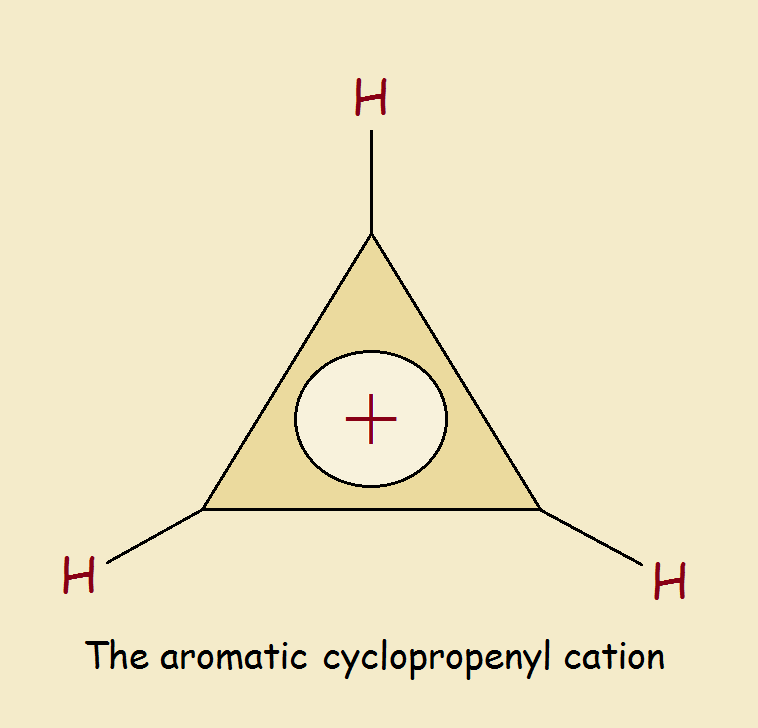
Aromatic Cyclopropenyl Cation Huckel S Smallest Example

Oneclass 1 Classify The Following Compounds As Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic 8 Points P
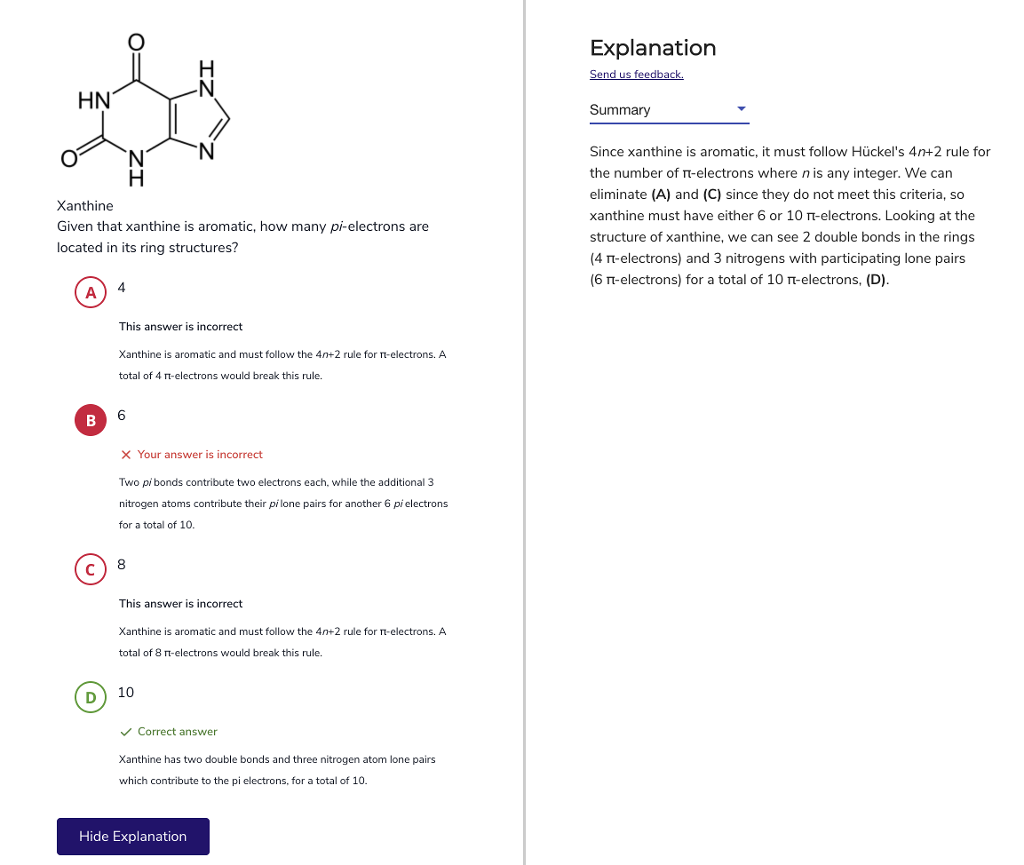
Solved Can Someone Further Explain This To Me Please I D Chegg Com
Mobius Aromatics Arising From A C C C Ring Component
Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry
Aromatic Stability Iii Video Khan Academy

Huckel S Rule Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep
Antiaromaticity And Antiaromatic Compounds Master Organic Chemistry

Organic Chemistry Final Exam 24 Questions With Answers Chem 14c Docsity

Benzene And Aromaticity
Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry

Solved Aromaticity Worksheet Chem 2410 Fall 19 Determin Chegg Com
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term
Huckel Aromaticity And Frost Circles Organic Chemistry Help
According To Huckel Rule An Aromatic Compound Must Possess

Mobius Aromaticity Wikipedia
Does Huckel S Rule Hold True For All Organic Compounds Or It Has Certain Limitations Quora
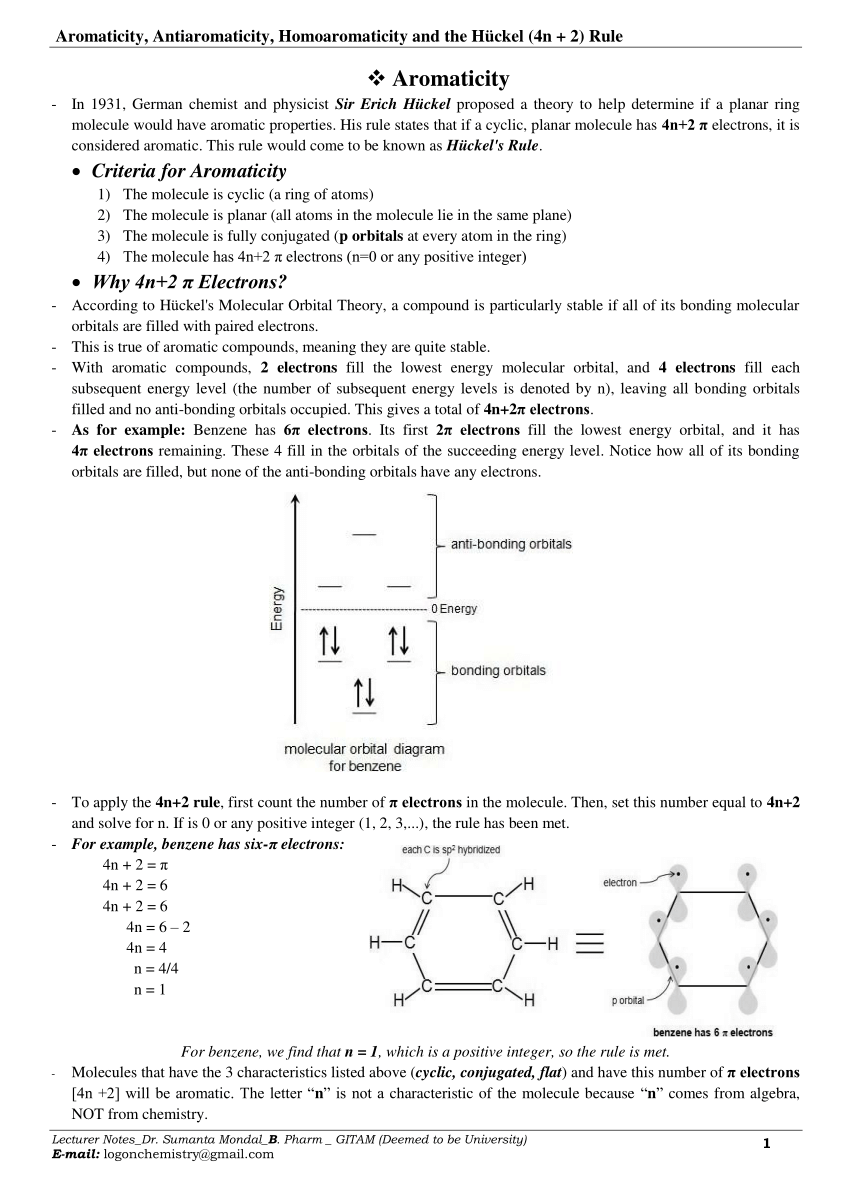
Pdf Aromaticity Antiaromaticity Homoaromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule

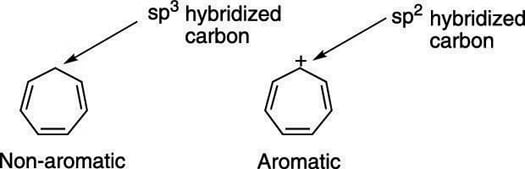
Why Is Cyclopropene Non Aromatic Quora
Pictures Of The Day
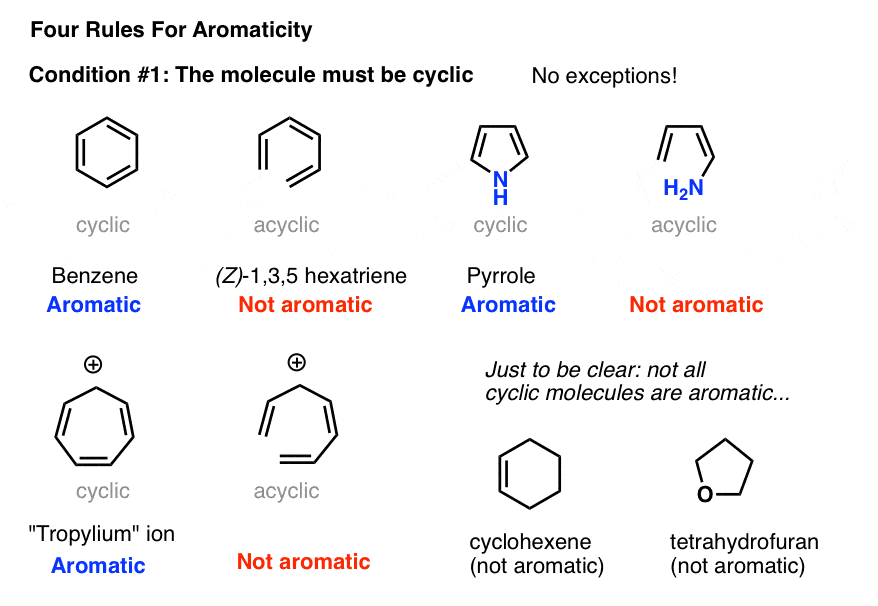
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry

Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Heterocycles Aromaticity Youtube

Identifying Aromatic Compounds Organic Chemistry
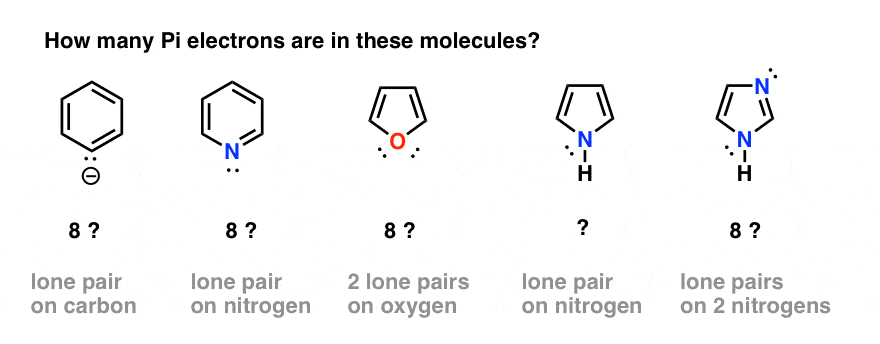
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry

Benzene And Aromaticity

Which Of The Following Structures Qualify As Being Aromatic According To Huckel S Rule Homeworklib

Quantum Chemistry 14 4 Huckel S Rule Youtube
Huckel S Rule For Aromaticity Time Saving Shortcut Youtube
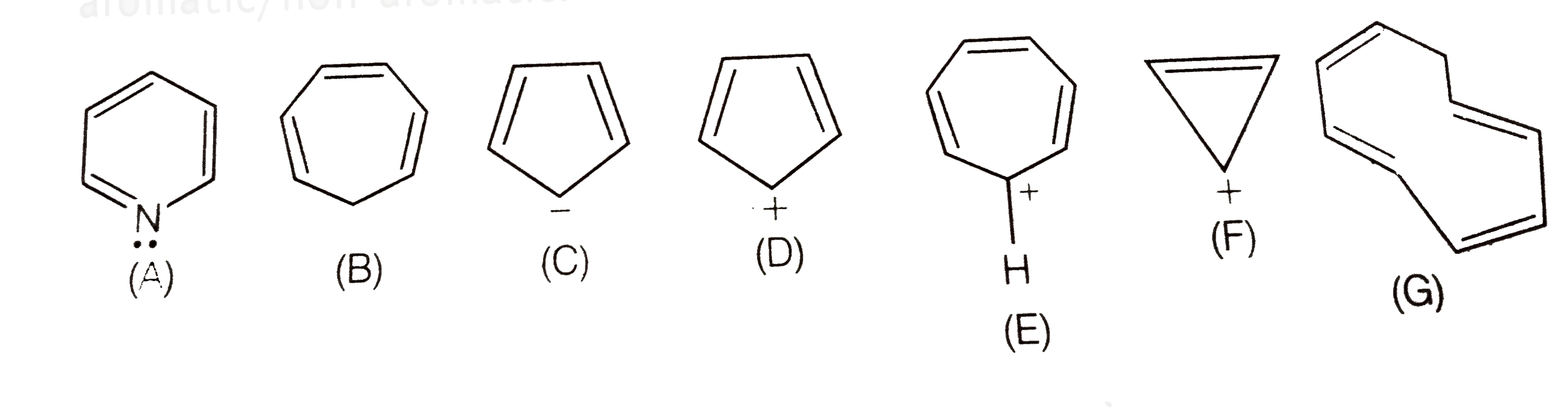
The Ring Systems Having Following Characteristics Are Aromatic B

What Is An Aromatic Compound Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Solved Aromatic Molecules Contain Pi Electrons A 4n Chegg Com
Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download
Aromaticity Rules And Definition Organic Chemistry Help

Indicate Whether Each Structure Is Aromati Clutch Prep

Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Heterocycles Aromaticity Youtube
How To Determine The Aromaticity Of A Ring System Dummies
What Are Aromatic Compounds Socratic
Aromaticity 4 Criteria Every Compound Needs
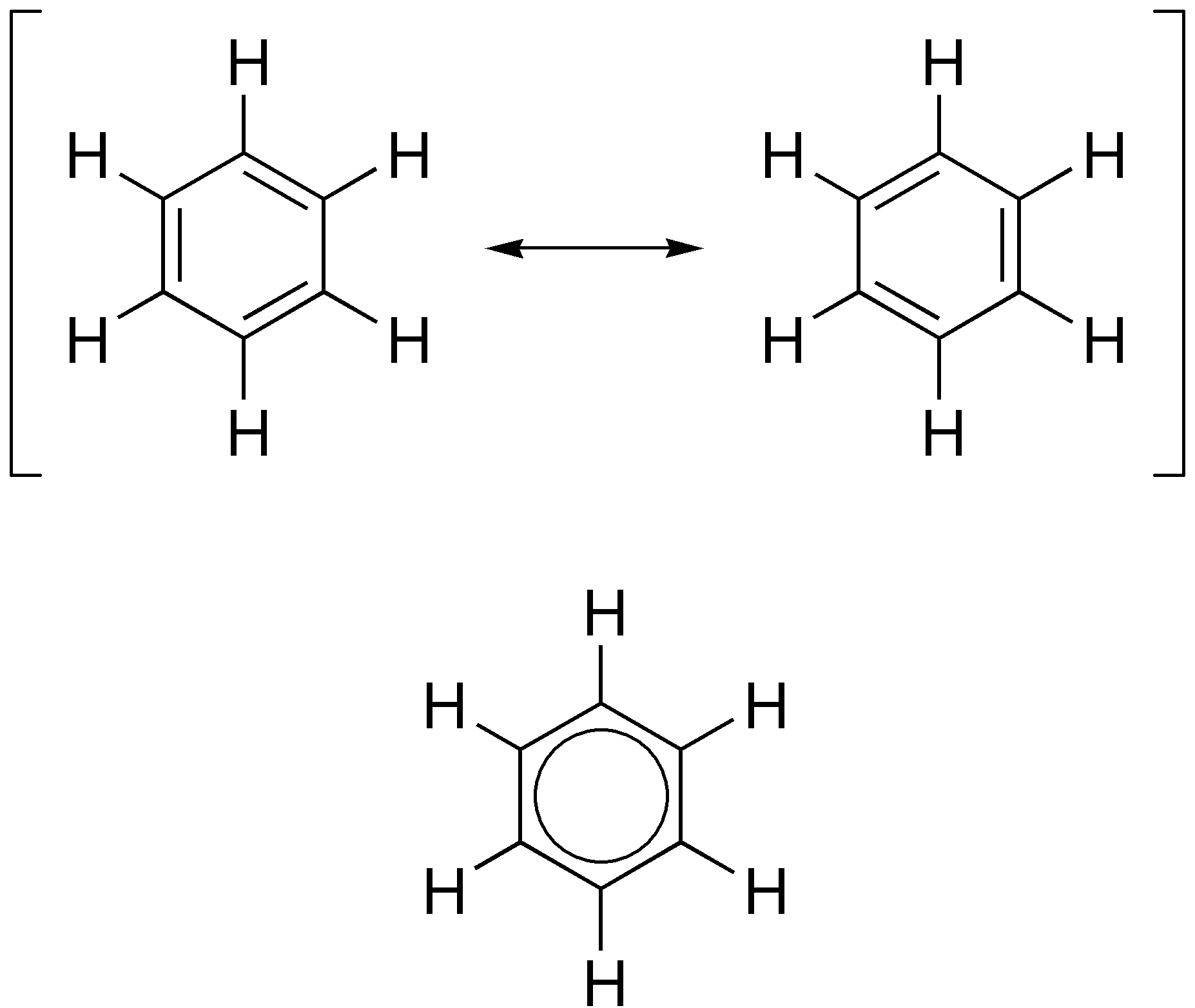
Aromaticity Wikipedia
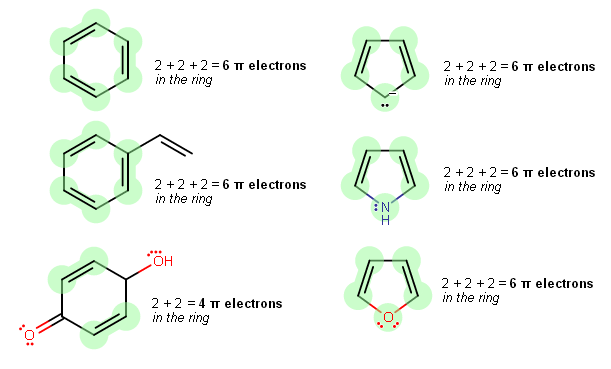
How Do You Count Pi Electrons In Aromatic Compounds Socratic
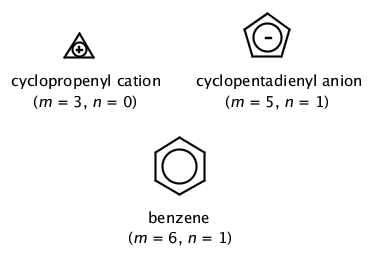
Iupac Huckel 4 Em N Em 2 Rule H

What Is An Aromatic Compound Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Quantum Chemistry 14 4 Huckel S Rule Youtube
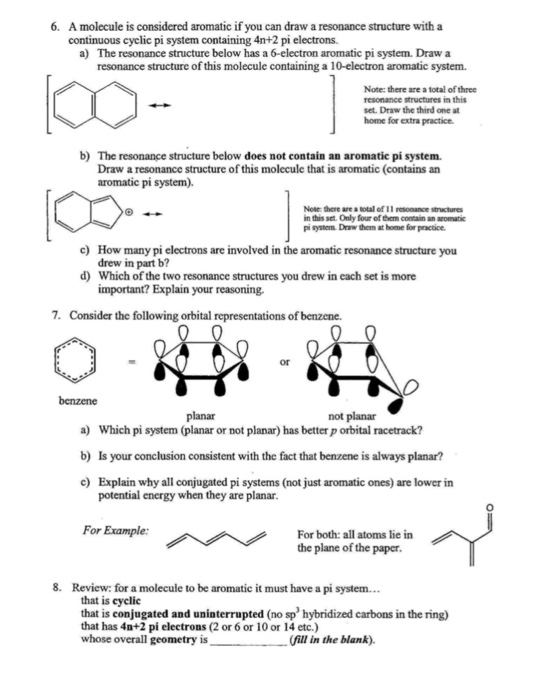
Solved Figure 2 Not All Cyclic Conjugated Pi Systems Are Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gctsibpu9kf Zrkgydy2ruhr8wfzjgykiyuqofmku5qe7yymfpwb Usqp Cau

Oneclass 2 3 Diphenylcyclopropenone See Structure Below Forms An Addition Product With Hbr That E
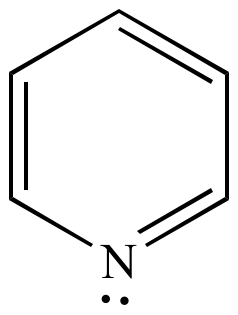
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term
Aromatic Stability Of Benzene Video Khan Academy
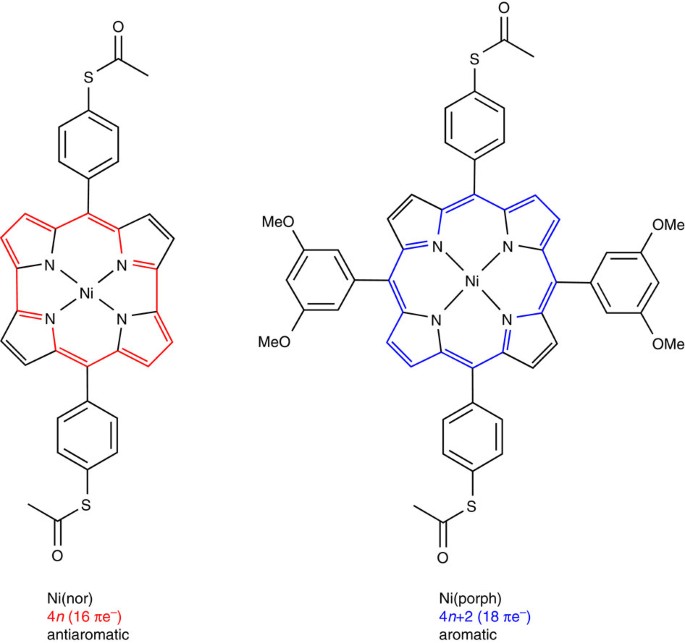
Highly Conducting Molecular Circuits Based On Antiaromaticity Nature Communications

Aromatic Stability Ii Video Khan Academy

Solved 1 According To Huckel S Rule How Many Pi Electro Chegg Com

Directivity And Ring Activation Deactivation Ppt Video Online Download

13 6 Aromaticity Organic Chemistry Ii
Aromatic Stability I Video Khan Academy

Aromatic Properties Mcat Question Of The Day

Huckel S Rule Definition Formula And Examples
Pericyclic Reaction Selection Rules
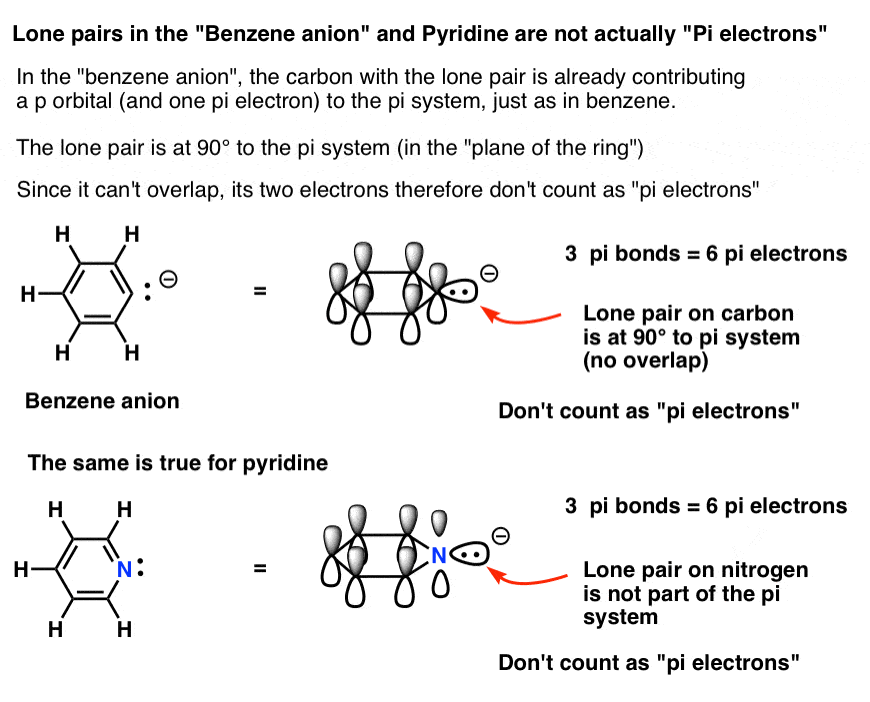
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
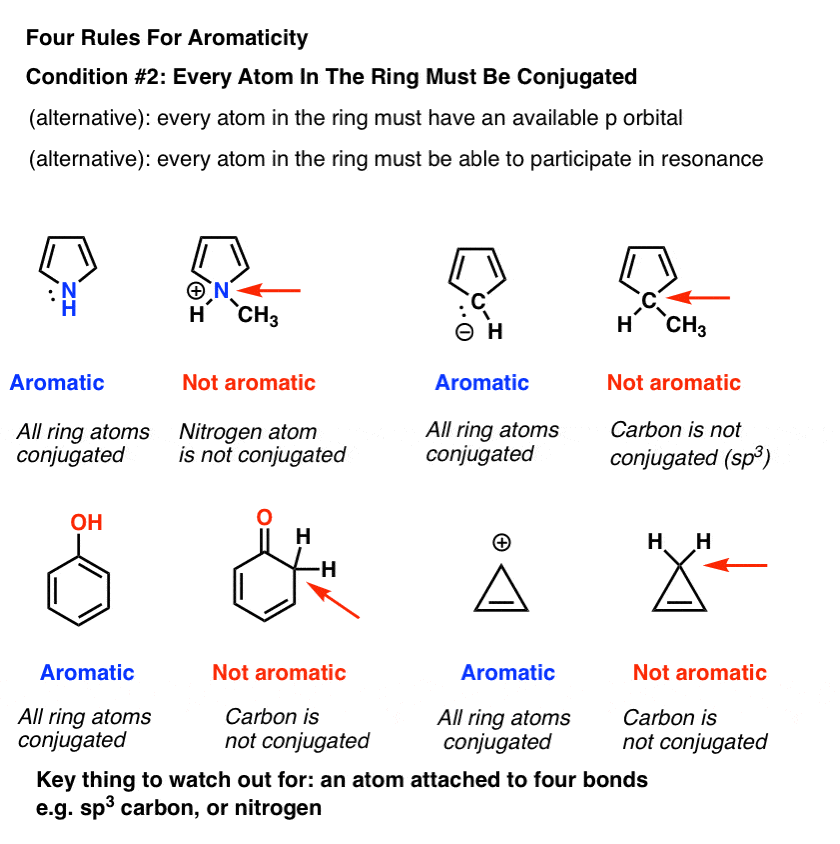
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry

Chapter 17 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download
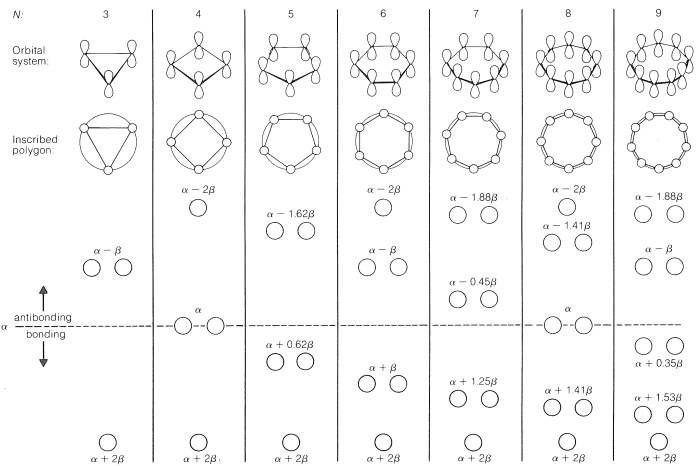
21 10 Huckel S 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts
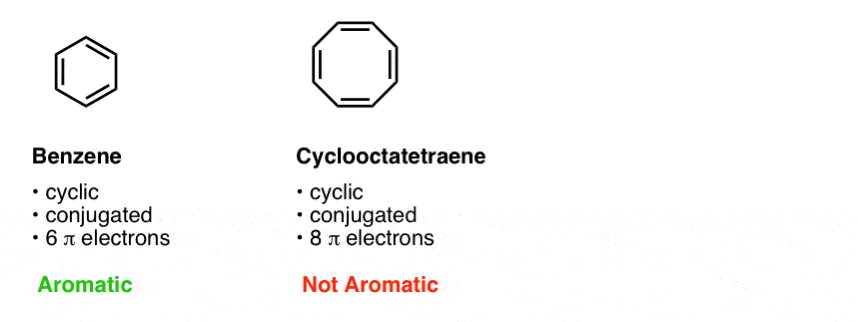
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
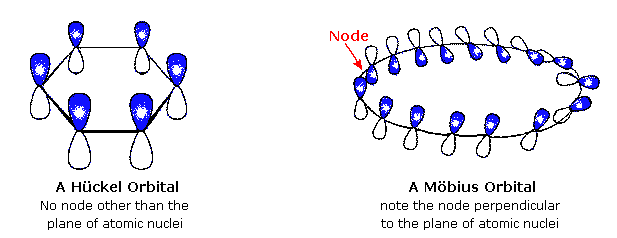
A Mobius 16 Pi Electron System
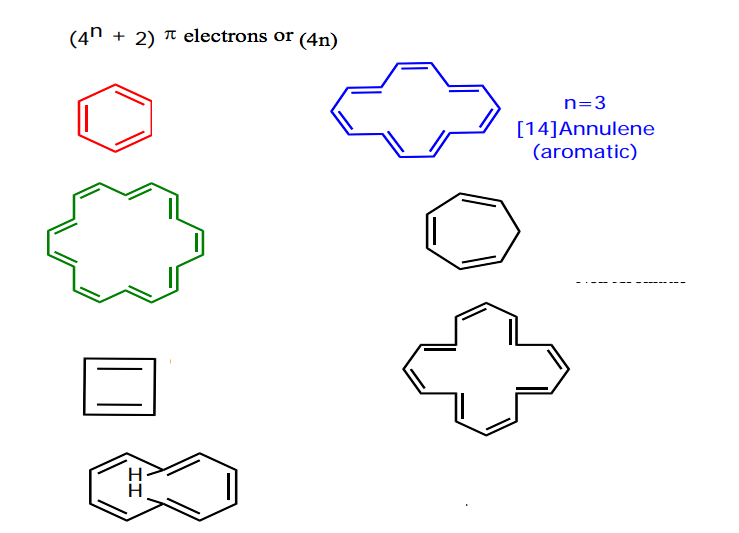
Solved 4 N 2 Pi Electrons Or 4 N Chegg Com

13 6 Aromaticity Organic Chemistry Ii

Antiaromatic Molecule Displays Record Electrical Conductance
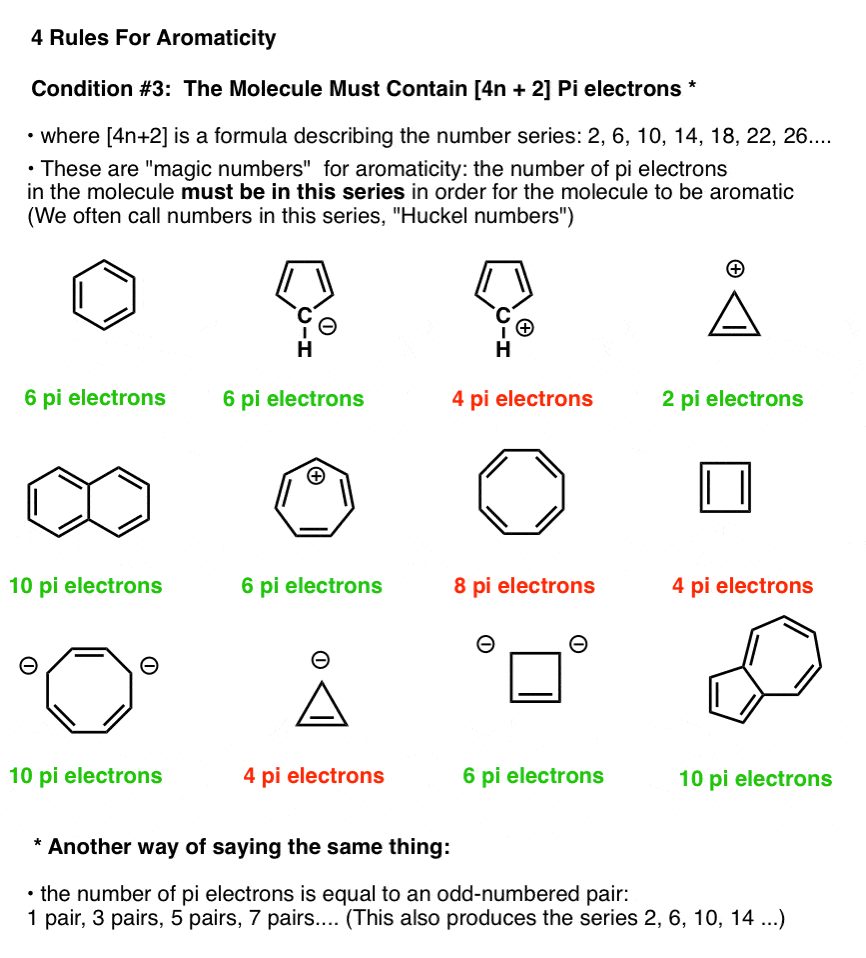
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
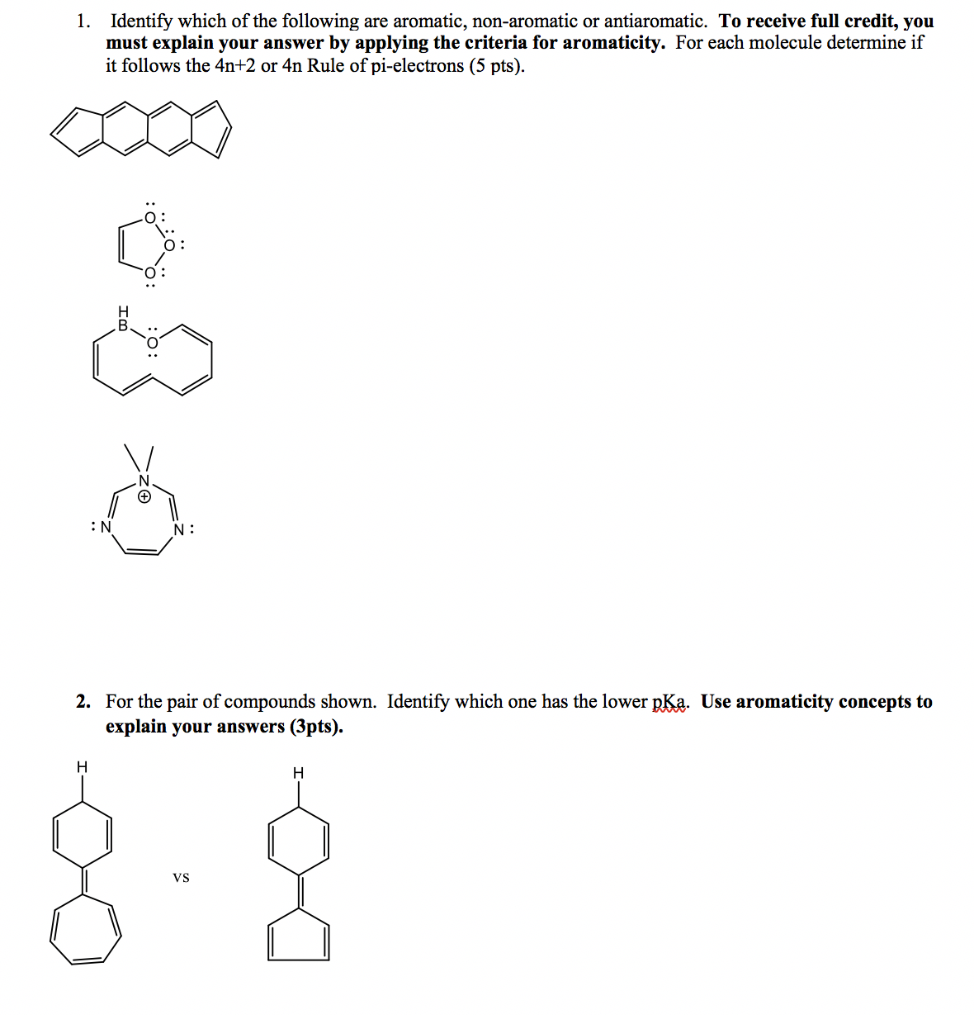
Solved 1 Identify Which Of The Following Are Aromatic N Chegg Com

Solved Why Is The Following Compound Not Aromatic Oit Is Chegg Com

The Criteria For Aromaticity Mcc Organic Chemistry
Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Non Aromatic 13 Worked Examples
The Problem With Pyrene Michael J S Dewar To The Rescue
Solved Please Help Me Solve These 3 Questions Also For Chegg Com
Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry
Huckel S Rule Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep
Ch 14 2 Characteristics Of Benzene Ppt Download

Identifying Aromatic Compounds Organic Chemistry
Aromatic Compounds Who Really We Are
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry

Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Non Aromatic 13 Worked Examples
1
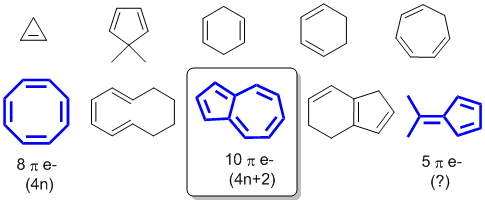
Multiple Choice Answers 353 Fin W17
Aromaticity Rules Cssac
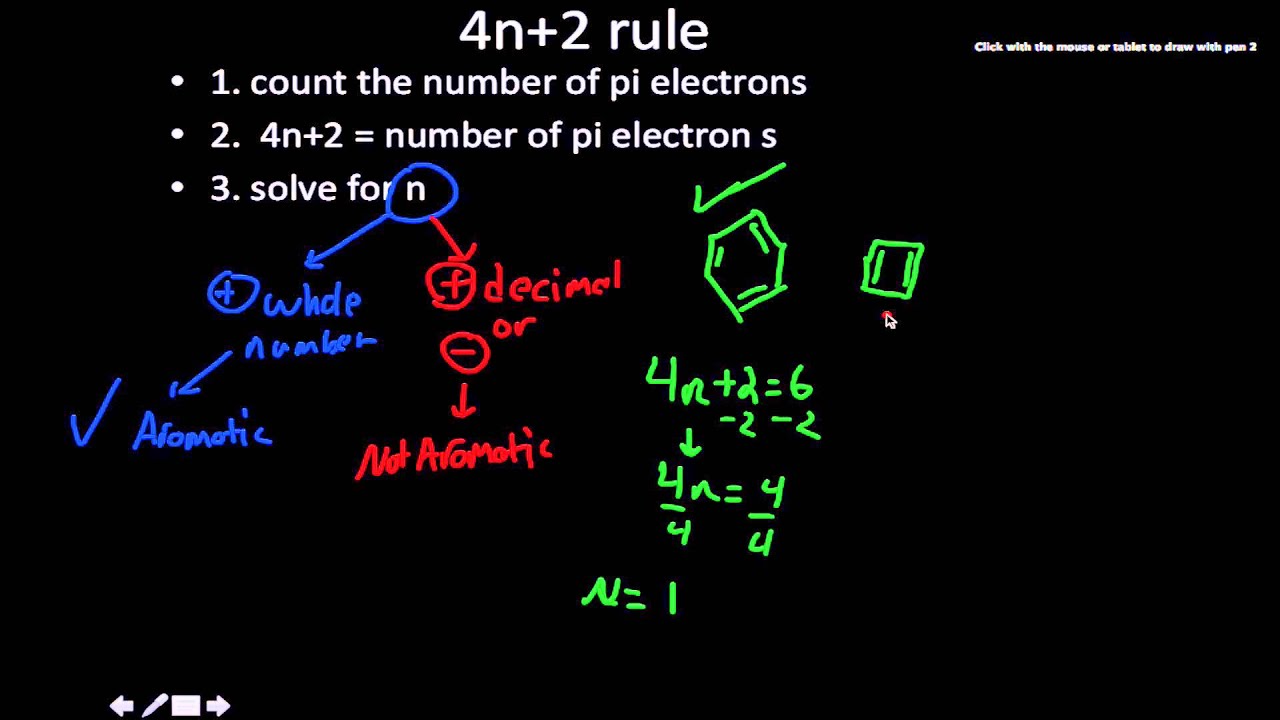
4n 2 Rule Youtube
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsd3ah2vdmhe7uydhdx6apoxlogkcmi2fl06j52sg1i2jna0doq Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqpcodx2bi5jpopeynalgtatdsd1mbfuenuzhd39c3vn4zej3xa Usqp Cau
How Is Anthracene Aromatic Quora
Mafiadoc Com Download Aromaticity 5c2634b3097c47a9028b45be Html
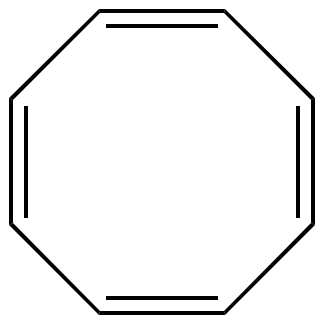
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term
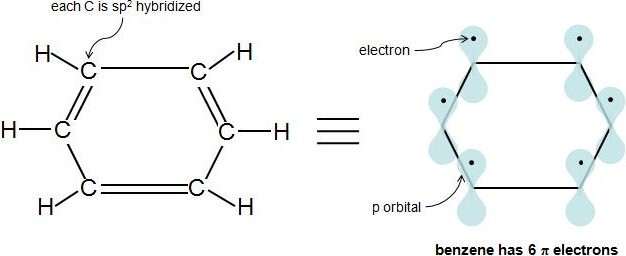.jpg?revision=1)
15 4 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts
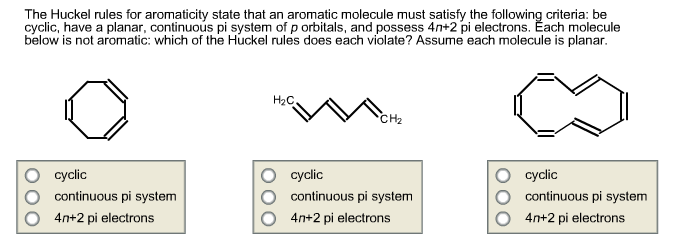
Solved The Huckel Rules For Aromaticity State That An Aro Chegg Com
Aromatic Stability Iii Video Khan Academy

Is Tropone Aromatic Chemistry Stack Exchange
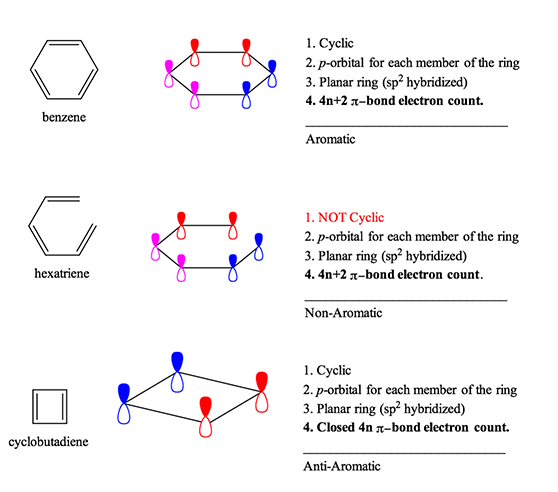
Aromaticity Rules And Definition Organic Chemistry Help

Indeno 1 2 B Fluorene Based 2 2 Cyclophanes With 4n 4n And 4n 4n 2 P Electrons Syntheses Structural Analyses And Excitonic Coupling Properties Wang 19 Angewandte Chemie Wiley Online Library



