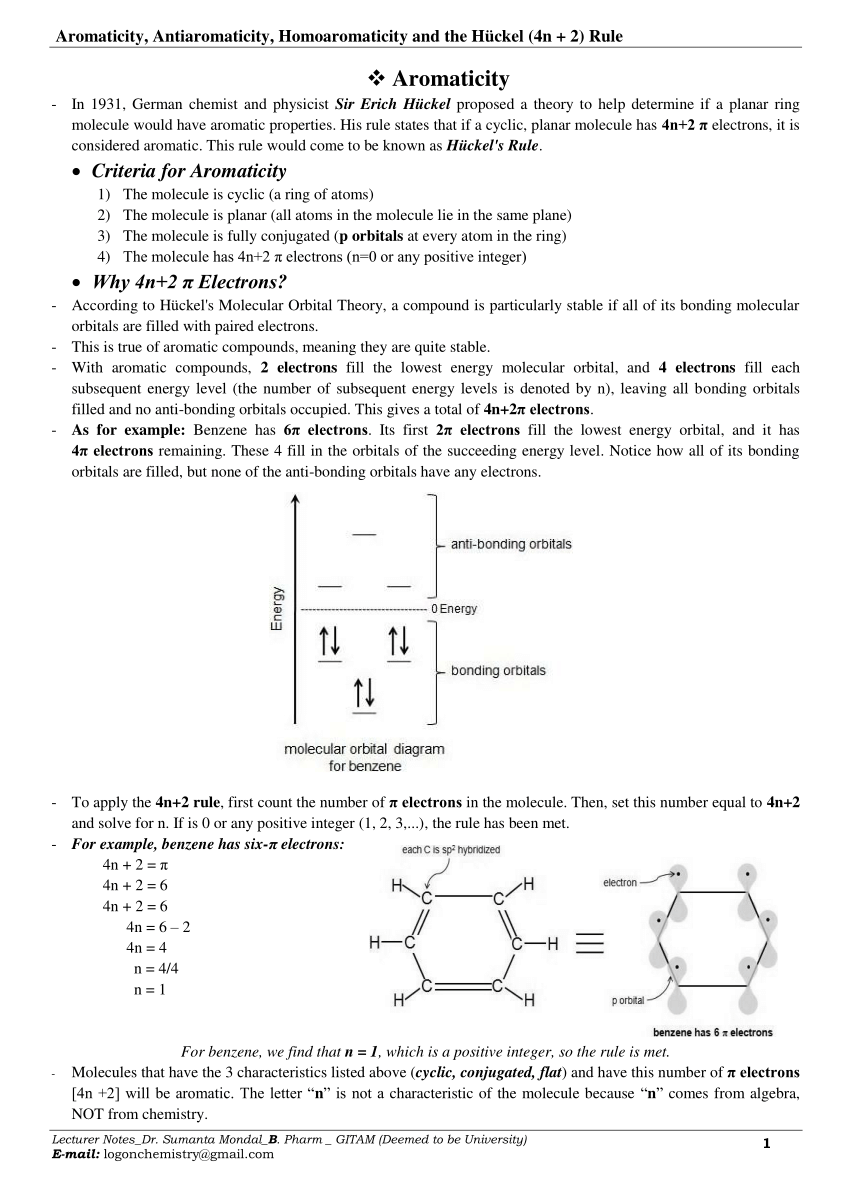
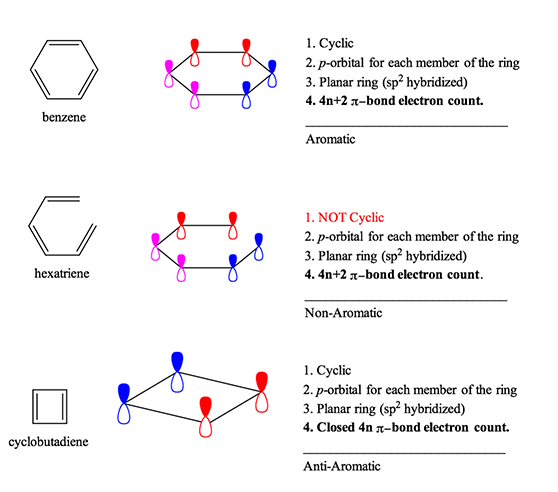
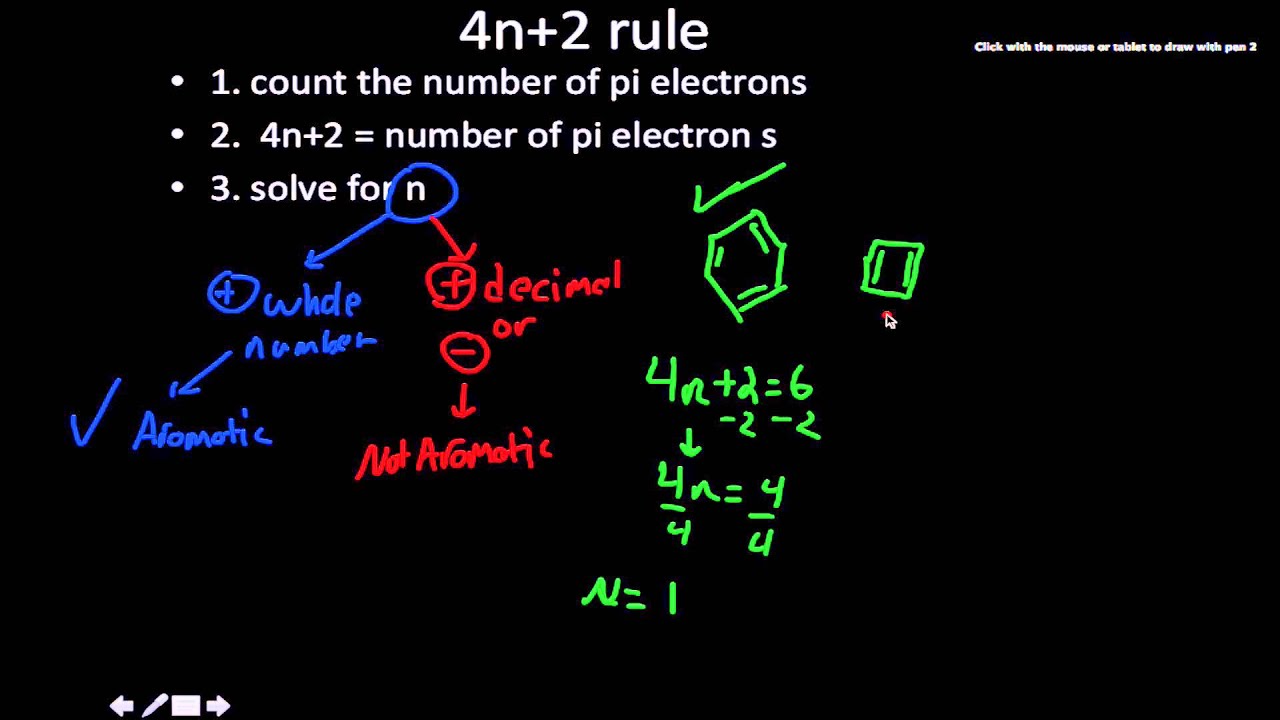
4n+2 Rule
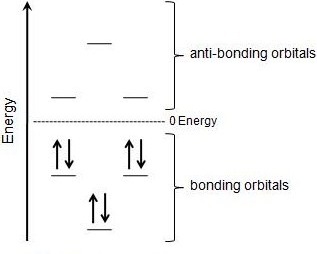
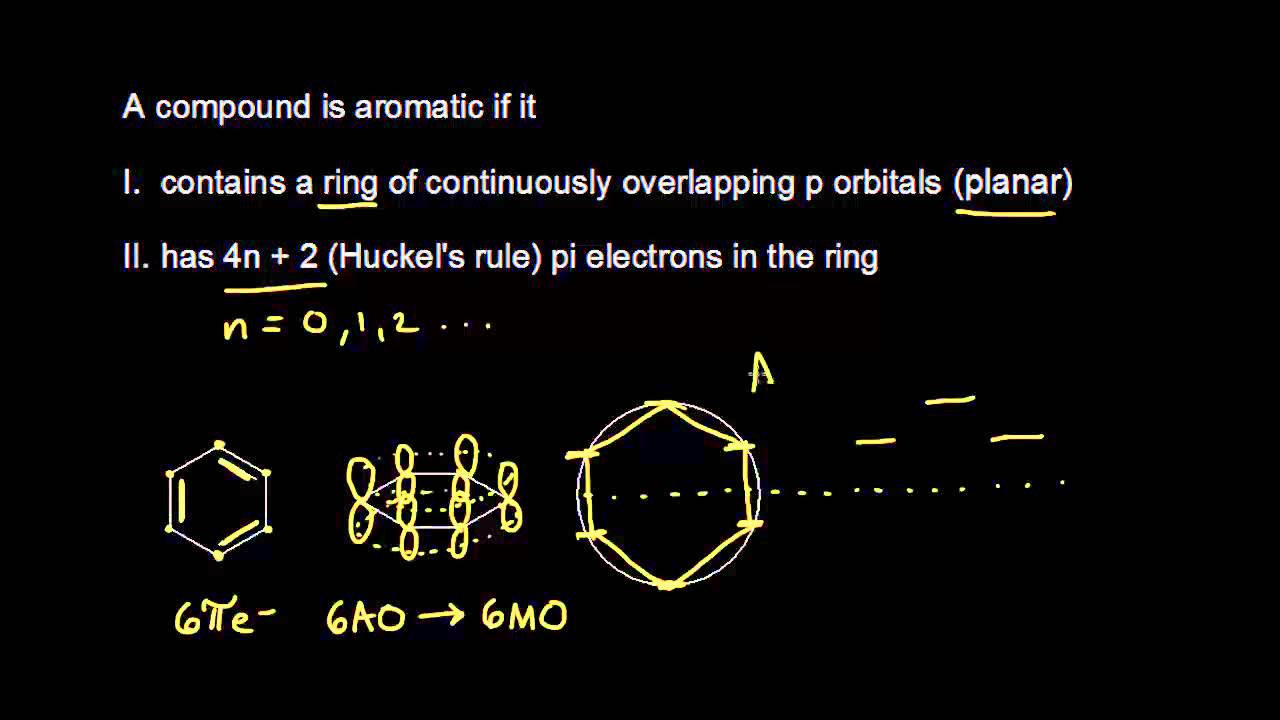
Aromatic compounds contain 4n+2 π electrons, where n is a whole number starting from 0.

4n+2 rule. A refinement specific to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) is Clar's rule. An aromatic compound must have a molecule that contains cyclic cloud of Delocalized π electrons and the π cloud must contain a total of (4n+2) π electrons. Define aromaticity in terms of the Hückel 4 n + 2 rule.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. In 1930 Erich Huckel proposed a rule name Huckel’s rule or (4n+2) rule. Huckel's Rule (4n+2 rule):.
Huckel, who devised the simple form of molecular orbital theory we have described in this chapter. This rule is the work of the German theoretician, E. Let’s understand it by taking the example of Benzene and Cyclo octa-tetraene.
Huckel’s rule is used to identify the Aromaticity of a compound. Can 4n+2 equal six, given the restrictions on the value of n?. Parabola, Finding the Vertex :.
4n+2 = Number of Resonating Electrons. Describe the difference in properties between an aromatic hydrocarbon. Resonating electrons include both pi electrons and lone pairs.
An aromatic compound must have a molecule that contains cyclic cloud of Delocalized π electrons and the π cloud must contain a total of (4n+2) π electrons. 휘켈 규칙(Hückel's rule)은 유기 화학에서 평면 고리 분자가 방향족성을 띠게 되는 조건에 대한 규칙이다. The nature of the occupied π orbitals must always be examined.
Before understanding the Huckel’s rule, you need to have a good understanding of aromaticity. If we get a fraction then the molecule DOES NOT obey Huckel’s rule. Hückel (4 n + 2) rule.
Then, set this number equal to 4n+2 and solve for n. Therefore, the K(4n + 2) rule is of rather limited range and the table given in Ref. These are depicted in Fig.
Earlier we factored this polynomial by splitting the middle term. 10/10/19 1 15.3 AROMATICITY AND THE HUCKEL 4N + 2 RULE Objectives After completing this section, you should be able to 1. These bond angles (140°) differ significantly from the ideal angles of 1°.
It does not have a cycle of rt bonds. A compound to become aromatic should obey Huckel’s rule. The pi electron count is defined by the series of numbers generated from 4n+2 where n = zero or any positive integer (ie, n = 0, 1, 2, etc.).
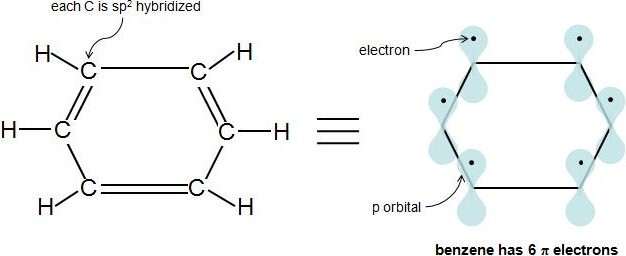
For example, benzene has six π electrons:. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. It was first expressed succinctly as the 4n+2 (actually 2+4n) rule by von Doering in 1951.
2, 6, 10, 14 etc. It is not planar It does not have an electrons. To apply the 4n+2 rule, first count the number of π electrons in the molecule.
Have a closed loop of 4n+2 pi-bond electrons, where n is equal to any integer (0,1,2,3,…) But like most natural phenomenon, there exists a rule exactly the opposite. 폰 되링이 1951년 4n+2꼴을 밝혀냈다. A Pedestrian Approach to the Aromaticity of Graphene and Nanographene:.
When n = 1, for example, there are six pi-electrons, as for benzene. Use the Hückel 4 n + 2 rule to determine whether or not a given polyunsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon should exhibit aromatic properties. Oila, benzene satisfies Huckel's rule.
The Huckel aromaticity rules are:. Draw the resonance structures for cycloheptatriene anion. Download my free guide ’10 Secrets to Aci.
The "4n + 2 rule" is derived analytically at the level of the simple Hückel theory for neutral even-membered chains, their double ions, as well as cations and anions of the odd-membered chains, by determining the first order energetic effect of the ring closure. A circle mnemonic predicts orbital energies for conjugated rings. Furthermore, the 4n+2 rule as indicator of aromatic stabilization should only be used in conjunction with the ring size;.
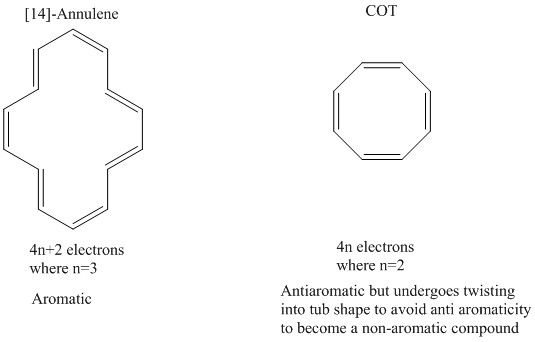
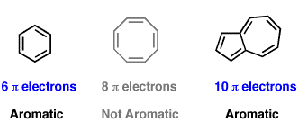
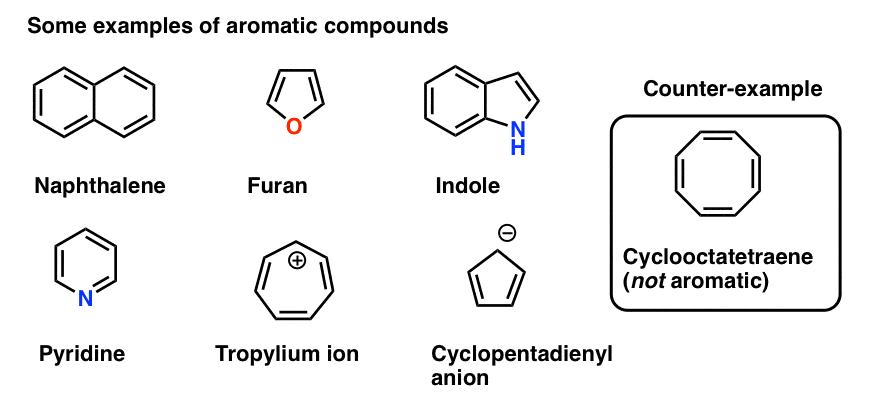
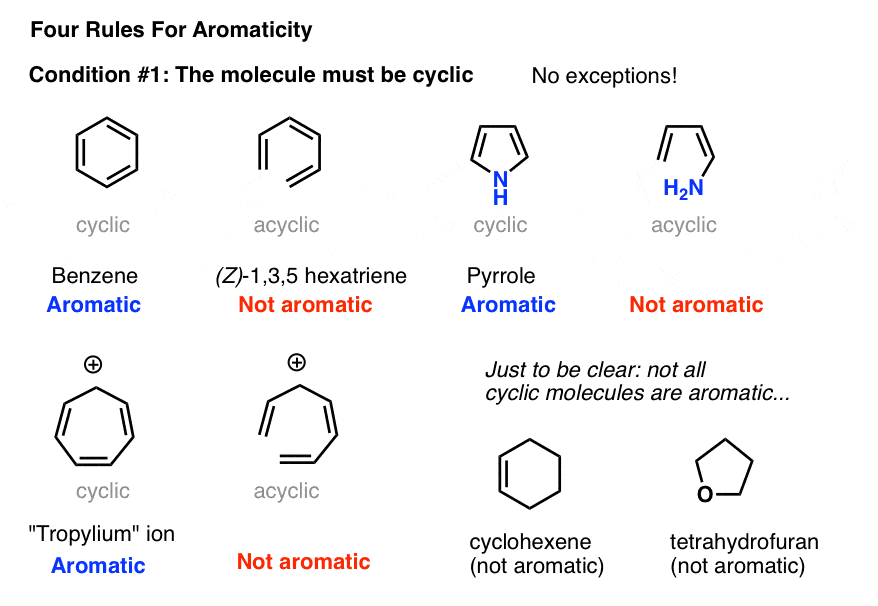
Both of these polycyclic molecules are aromatic even though they fail the 4n + 2 rule. In organic chemistry, Huckel's rule estimates whether a planar ring molecule will have aromatic. A benzene ring has 3 pi bonds thus 6 resonating.
Indeed, Hückel's rule can only be theoretically justified for monocyclic systems. Significance of Huckel’s (4n+2)π Electron Rule. The Huckel 4n + 2 Pi Electron Rule.
Another way to put the 4n+2 rule is that if you set 4n+2 equal to the number of electrons in the pi bond and solve for n, you will find that n will be a whole number. Solving 4n 2 +4n+1 = 0 directly. This rule estimates whether a planar ring compound will possess aromatic properties or not.
Although its succinct formulation as 4n + 2 was given by Professor William von Eggers Doering. This is called the Hückel’s rule discovered by Erich Hückel in 1931. 물리화학자 에리히 휘켈이 1931년에 처음 연구하였다.
8 (cyclooctatetraenide anion), with ten π electrons obeys the 4n + 2 rule for n = 2 and is planar, while the 1,4-dimethyl derivative of the dication, with six π electrons, is also believed to be planar and aromatic. Monocyclic planar (or almost planar) systems of trigonally (or sometimes digonally) hybridized atoms that contain (4 n + 2) π-electrons (where n is a non-negative integer) will exhibit. Therefore n must be a whole number that satisfies this equation 4n+2=x, where x = the number of electrons in the pi bonds.
Let us now solve the equation by Completing The Square and by using the Quadratic Formula. The last one is that the organic compound has to be flat. In 1930 Erich Huckel proposed a rule name Huckel’s rule or (4n+2) rule.
When solving for ‘n’, n must equal to a whole number. It follows the same 4n+2 rule as for benzene, but this time counting the electrons involved in the reaction rather than just the π-electrons in the aromatic ring. 4.1 Find the Vertex of y = 4n 2 +4n+1 Parabolas have a highest or a lowest point called the Vertex.
The advantage of this approach is that aromaticity is quite stable to perturbations to the symmetry (benzene rings in e.g. If is 0 or any positive integer (1, 2, 3,), the rule has been met.-For example, benzene has six-π electrons:. The topological background of the "4n + 2 rule" is also briefly discussed.
To apply the 4n+2 rule, first count the number of π electrons in the molecule. Huckel arrived at this rule by performing molecular orbital calculations on cyclic systems containing x carbon atoms, and with each carbon atom supplying one pi electron. The “4n + 2 rule” is derived analytically at the level of the simple Hückel theory for neutral even-membered chains, their double ions, as well as cations and anions of the odd-membered.
Why is cyclooctatetraene not antiaromatic?. Number of times cited according to CrossRef:. According to Huckel’s rule, any specie that is cyclic, planar and has (4n+2) delocalized Ï€ electrons will be aromatic and stable.
How do you write {eq}(4n)^2 {/eq} without exponents?. Be planar, in an sp2 hybridized orbital, over every atom of the ring;. A cyclic ring molecule follows Hückel's rule when the number of its π electrons equals 4n + 2 where n is zero or any positive integer (although clearcut examples are really only established for values of n=0 up to about 6).
If is 0 or any positive integer (1, 2, 3,), the rule has been met. Pyrene is a commonly used counter-example of Hückel's rule. Schlegel diagrams of buckminsterfullerene (top diagram) and four of its isomers which can be built from naphthalene units.
A ring-shaped cyclic molecule is said to follow the Huckel rule when the total number of pi electrons belonging to the molecule can be equated to the formula ‘4n + 2’ where n can be any integer with a positive value (including zero). The 4n+2 rule dats da Huckel's Rule. Huckel's rule can become a little bit tricky when cations and anions are being evaluated for aromaticity.
Zexing Qu, Chen Yang, and Chungen Liu. It is not cyclic. \\begin{align} 4n + 2 &= 6 \\ 4n &= 4 \\ n &= 1 \end{align}\.
N= 0, 1, 2, 3, 4…etc.). Huckel’s rule was given by German physicist and physical chemistry Erich Huckel in 1931. For benzene, we find that n=1, which is a positive integer, so the rule is met.
Key IDEAS Hückel 4n + 2 Rule Some molecules with 4n 1 electrons are very unstable by virtue of being antiaromatic. Also known as Hückel's rule. 4n + 2 = 6 4n = 4 n = 1.
The exponent is used to. Cyclophanes for example can be bent by up to 30° and still. Huckel’s Rule for Aromaticity + Time-saving shortcut Need help with Orgo?.
The much greater stabilization in “aromatic” conjugated rings, and Hückel’s 4n+2 rule, derive from alternating stabilization and destabilization of successive orbitals when the ends of a conjugated chain overlap as it is closed to form a ring. The following molecule is aromatic?. Solid working knowledge of hybridization will help you tackle problems of this sort.
Huckel’s rule is used to identify the Aromaticity of a compound. According to Huckel’s rule, all planar aromatic compounds must have 4n+2 pi-electrons where n is an integer (i.e. Aromaticity plays a major role in the field of biochemistry of all the living structures.
As Huckel formulated, the latex 4n + 2 /latex rule applies only to monocyclic. The “4 n + 2 rule” is derived analytically at the level of the simple Hückel theory for neutral even-membered chains, their double ions, as well as cations and anions of the odd-membered chains, by determining the first order energetic effect of the ring closure. It is also known as Huckel’s 4n + 2 pi- electrons rule.
The exponent rule defines that the number of times a value or entity is multiplied with itself. For example, benzene has six \(\pi\) electrons:. In order to be aromatic , a molecule must have a certain number of pi electrons (electrons with pi bonds, or lone pairs within p orbitals) within a closed loop of parallel, adjacent p orbitals.
The topological background of the “4 n + 2 rule” is also briefly discussed. Why the structure is so stable is to be explained using resonance structures and the Huckel’s (4n+2) rule. (organic chemistry) Aromatic (ring) compounds must have 4 n + 2 pi-bonding electrons, where n is a whole number and generally limited to n = 0 to 5.
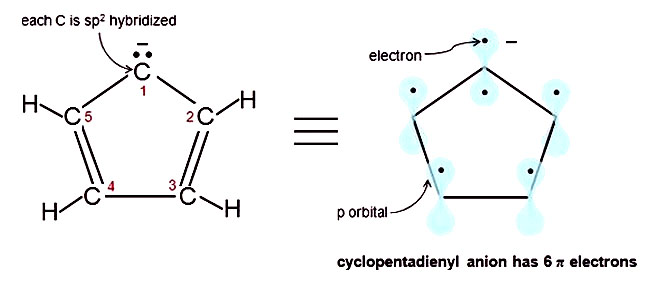
Simply put, Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that a monocyclic system will be aromatic if there are 4n + 2 delocalised electrons, (n an integer) contained within it. The theory is appropriately called Huckel MO theory, and the rule is Huckel’s latex 4n + 2 /latex rule. Cyclononatetraenide anion (C 9 H – 9) is largest all-cis monocyclic annulene/annulenyl system that is planar and aromatic.
Then, set this number equal to 4n+2 and solve for n. The $\ce{^{1}H}$ and $\ce{^{13}C}$ NMR spectroscopic characterization of the reported new cyclooctatetraene dications indicates these ions possess those characteristics expected of a $\ce{C8}$ 6 π aromatic system and hence further extends the evidence for the great predictive utility of the $4n+2$ Hückel rule. To be aromatic, a molecule must be planar conjugated, and obey the 4n+2 rule.
If is 0 or any positive integer (1, 2, 3,), the rule has been met. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 15, 119 (29) , -. Hückel's Rule In 1931, Erich Hückel postulated that monocyclic (single ring) planar compounds that contained carbon atoms with unhybridized atomic p orbitals would possess a closed bond shell of delocalized π electrons if the number of π electrons in the molecule fit a value of 4 n + 2 where n equaled any whole number.
Definitions of 4n 2 rule, synonyms, antonyms, derivatives of 4n 2 rule, analogical dictionary of 4n 2 rule (English). If n equals 1, then 4n+2 equals 6. (Theochem) 303 (1994) 2-286 285 Fig.
Definition of huckel's rule wit a lil mix of explanation :. 고리형 평면분자는 휘켈 규칙에 의해 그것의 파이 전자 수가 + (단 이 음 아닌 정수)일 때 방향족성을 띤다. All the compounds obey the Huckel’s Rule, i.e all the aromatic compounds should have the (4n+2) Pi number of electrons.
Benzene is the most common aromatic molecule.
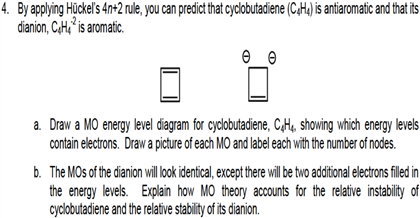
By Applying Huckel S 4n 2 Rule You Can Predict Th Chegg Com
2
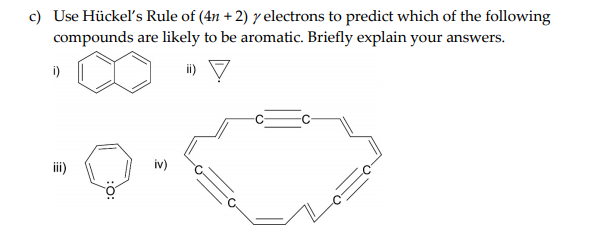
Solved Use Huckel S Rule Of 4n 2 Y Electrons To Predi Chegg Com
4n+2 Rule のギャラリー
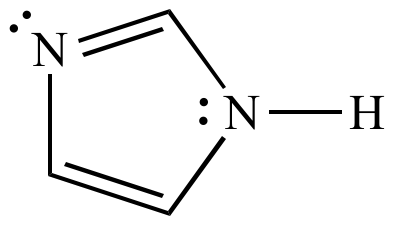
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term
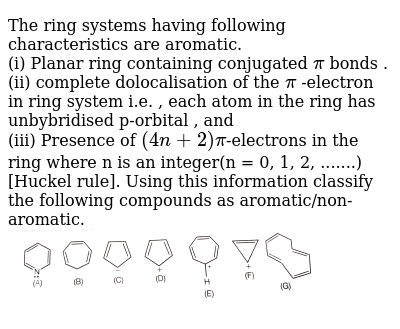
In Huckel S Rule 4n 2 P Electrons What Does N Signifies
Properties Of Aromatic Compounds Chemistry Revision Site
Mafiadoc Com Download Aromaticity 5c2634b3097c47a9028b45be Html

109 Aromaticity 2 Huckel S Rule Madoverchemistry Com
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=317&height=254)
Huckel S Rule Chemistry Libretexts
Pdf Aromaticity Antiaromaticity Homoaromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule
Solved 1 According To Huckel S Rule How Many Pi Electro Chegg Com

Cannot Pin Point The Other Ones 2 Identify Which Of The Following Compounds Is Aromatic And Homeworklib

Electrocyclic Reactions
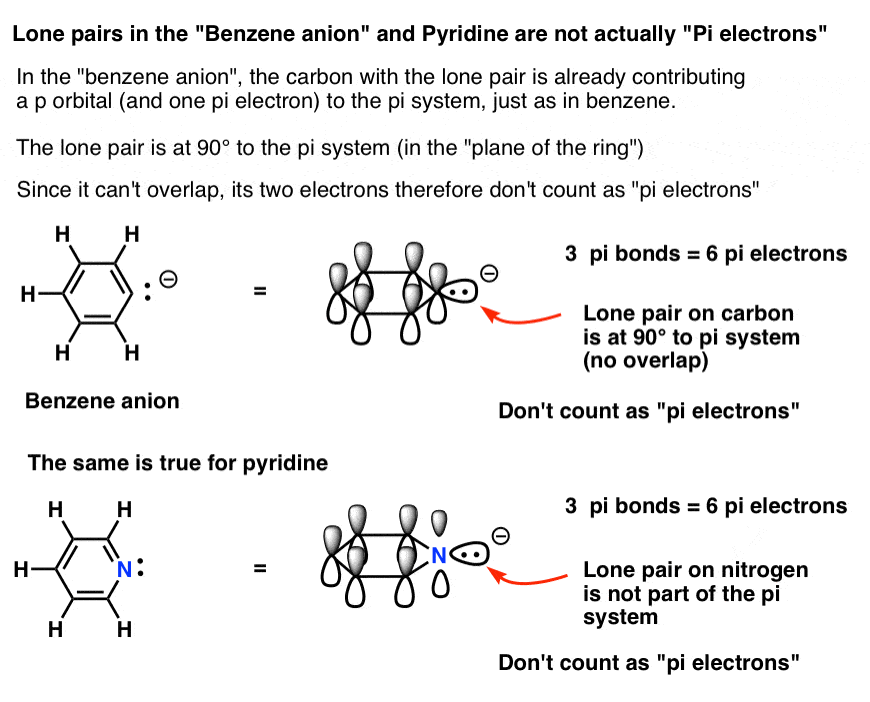
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqpcodx2bi5jpopeynalgtatdsd1mbfuenuzhd39c3vn4zej3xa Usqp Cau
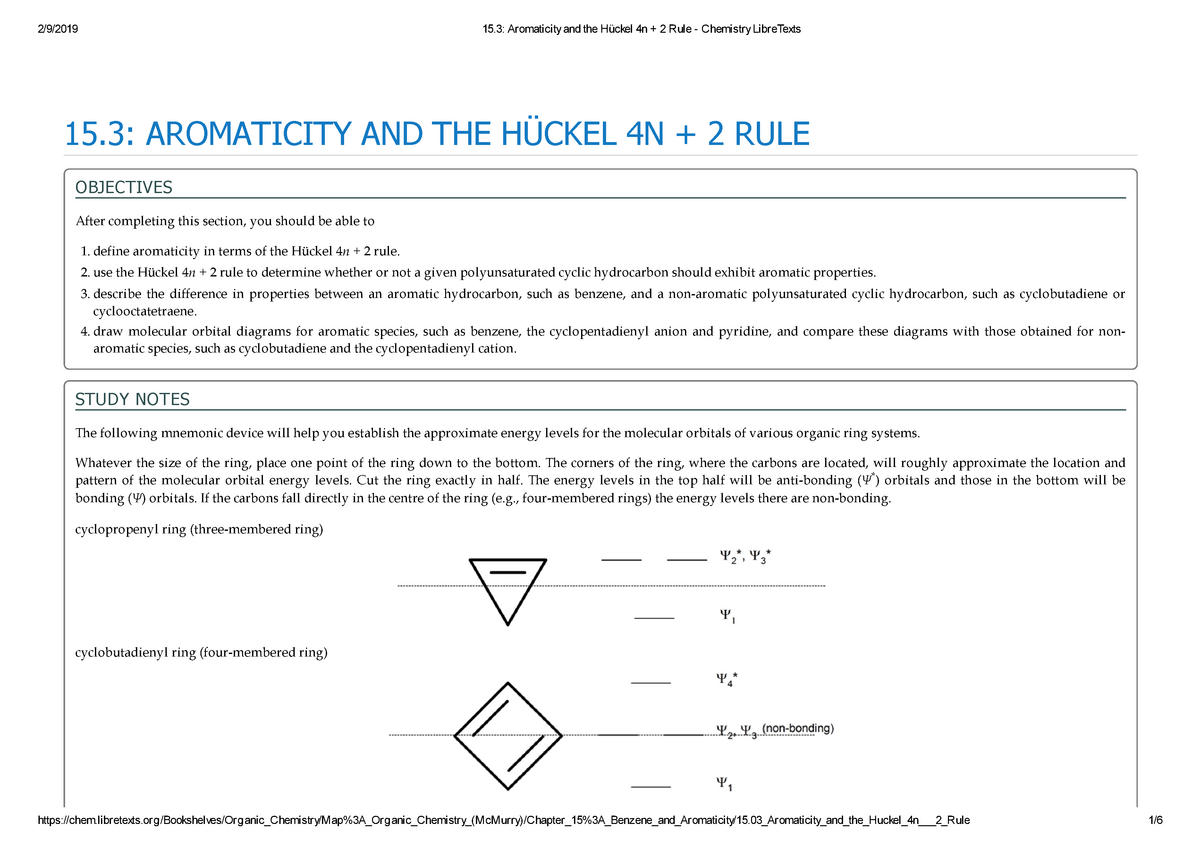
15 3 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libre Texts Studocu
Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 2f978 94 009 5718 3 2 Pdf
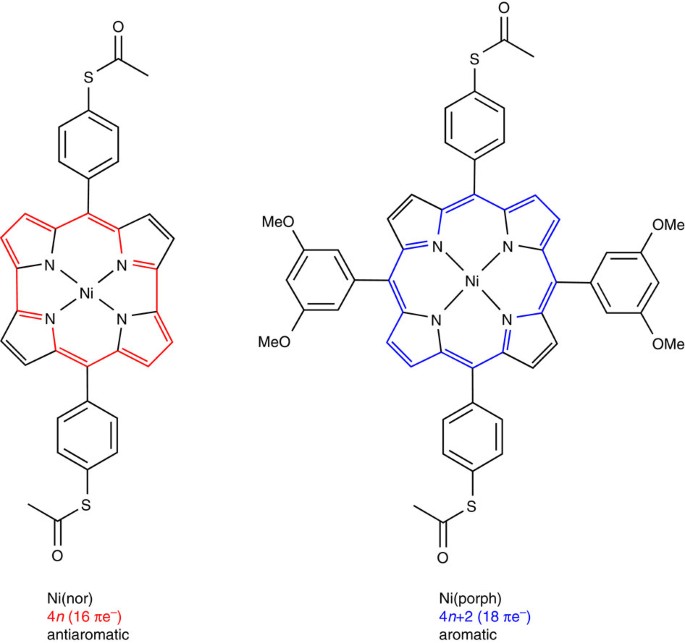
Highly Conducting Molecular Circuits Based On Antiaromaticity Nature Communications
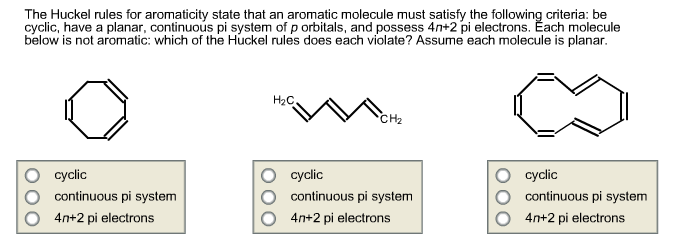
Solved The Huckel Rules For Aromaticity State That An Aro Chegg Com

Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Heterocycles Aromaticity Youtube
Aromaticity Rules And Definition Organic Chemistry Help
Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry

Huckel S Rule Definition Formula And Examples

Lecture 17 Chapter 15 Pdf Aromaticity Hckels 4n 2 Rule Only Applicable To Mono Cyclic Systems A Molecule Is Aromatic If 1 Every Atom In The Ring Has Course Hero
Q Tbn 3aand9gctn2msa8bylzftgwgj9seyexaol8il Rj7m Fddl7wiqxcdvypy Usqp Cau
Aromatic Stability I Video Khan Academy

15 4 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry

Huckel Rule Or 4n 2 Rule For Aromaticity Examples And Exceptions Youtube
4n 2 Rule Youtube

Quantum Chemistry 14 4 Huckel S Rule Youtube
.jpg?revision=1)
15 4 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts

A Disrotatory 4n 2 Electron Anti Aromatic Mobius Transition State For A Thermal Electrocyclic Reaction Henry Rzepa S Blog
Learn Aromatic 4n 2 Electrons Meaning Concepts Formulas Through Study Material Notes Embibe Com
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry

Mobius Aromaticity Wikipedia
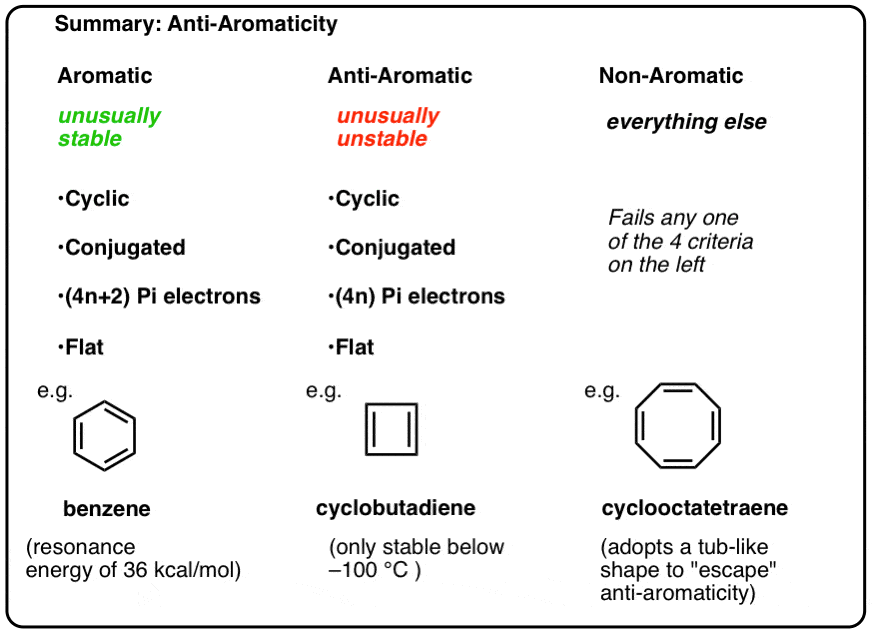
Antiaromaticity And Antiaromatic Compounds Master Organic Chemistry

The Concept Of Aromaticity Chempapy

13 6 Aromaticity Organic Chemistry Ii

13 6 Aromaticity Organic Chemistry Ii
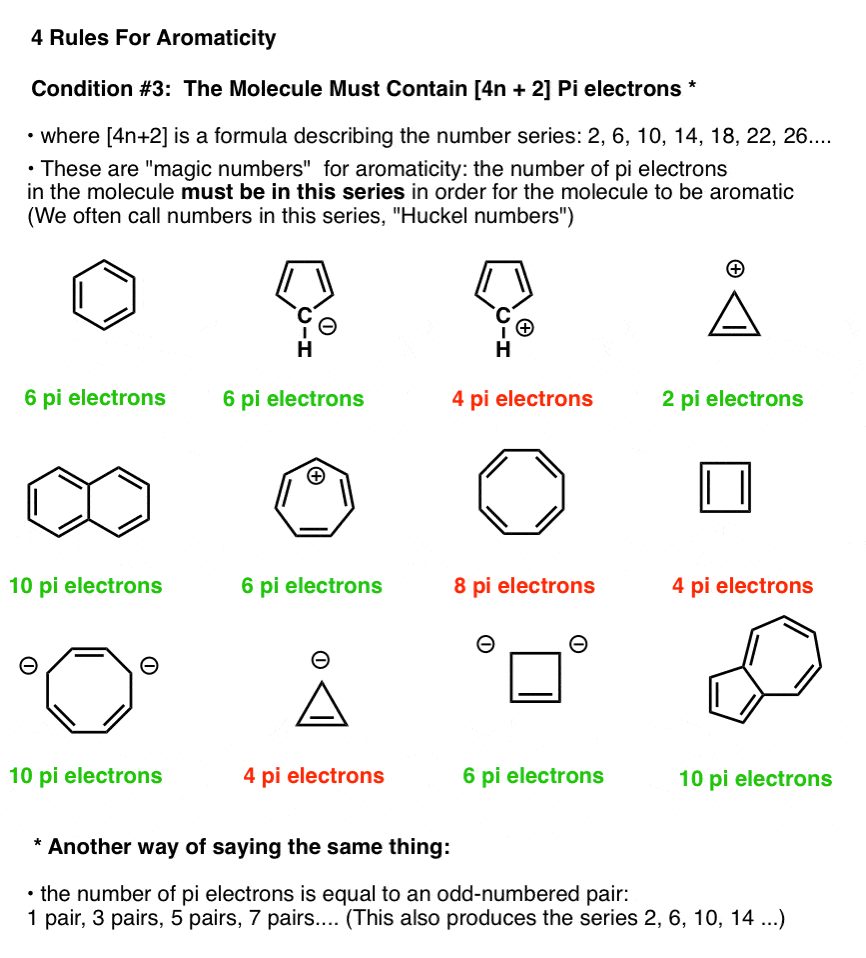
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
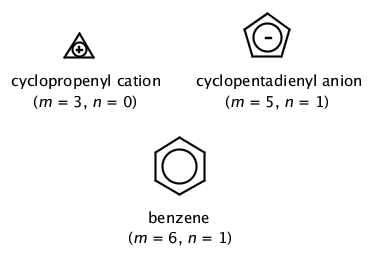
Iupac Huckel 4 Em N Em 2 Rule H
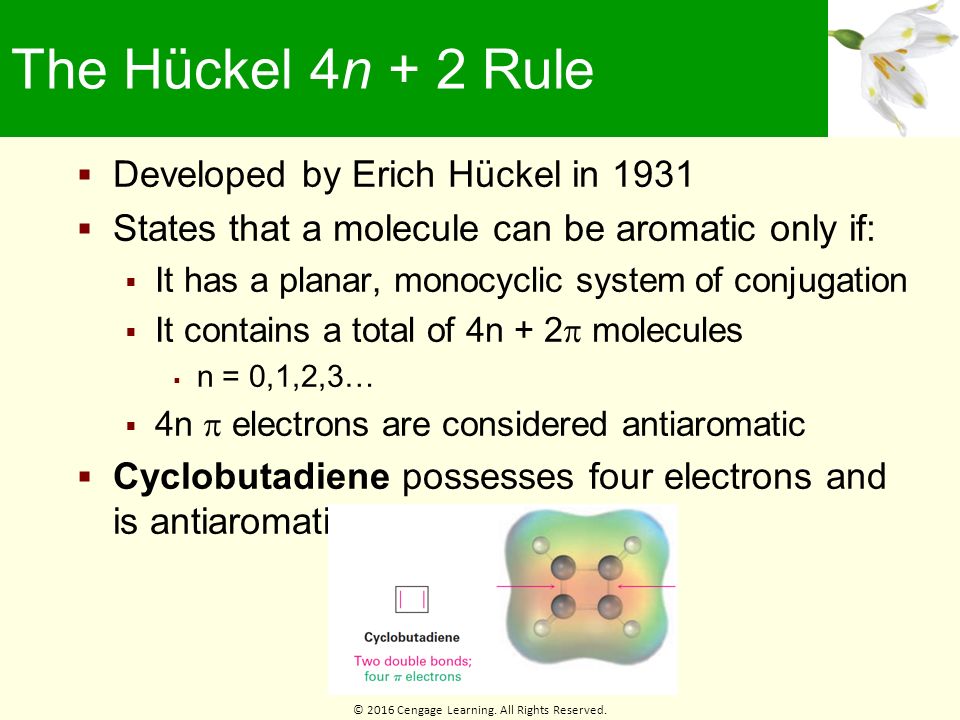
Chapter 15 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Download

Indicate Whether Each Structure Is Aromati Clutch Prep

Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps

Aromatic Properties Mcat Question Of The Day
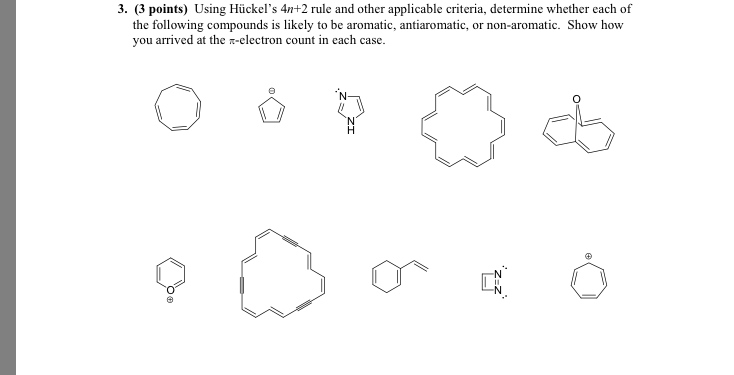
Solved Using Huckel S 4n 2 Rule And Other Applicable Cr Chegg Com

Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps

Aromaticity And Huckels Rule Powerpoint Slides

Chemistry Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Rule In Order To Be Facebook

Aromatic Compounds Ppt Video Online Download

The Criteria For Aromaticity Mcc Organic Chemistry

What Is An Aromatic Compound Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Term

Aromatic Compounds And Huckel S Rule Youtube
1
2

Huckel S Rule Aromatic And Antiaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps
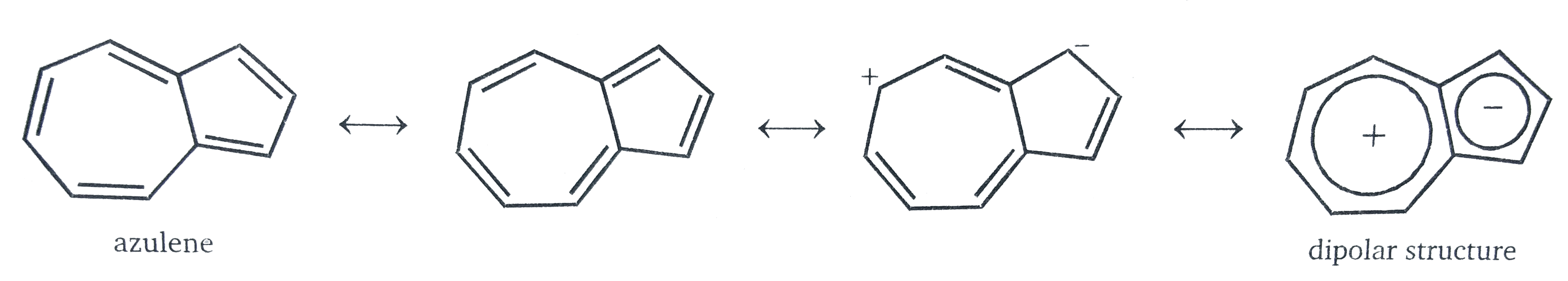
Which Compound Posses Highest Dipole Moment
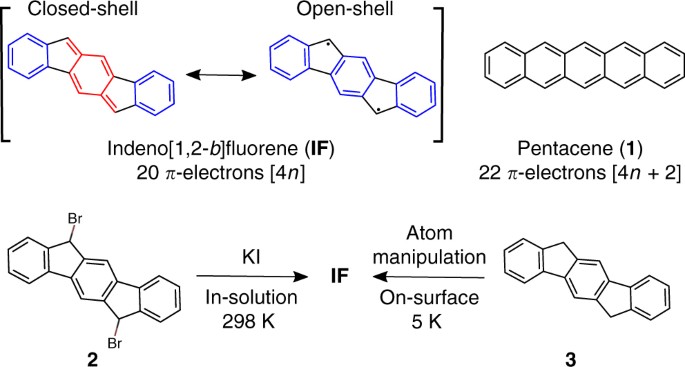
Studying An Antiaromatic Polycyclic Hydrocarbon Adsorbed On Different Surfaces Nature Communications

Pdf Analytical Derivation Of The Huckel 4 N 2 Rule

Chapter 17 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download
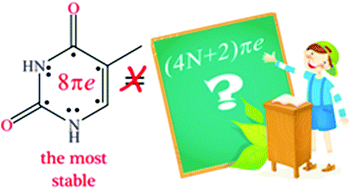
Tautomerisation Of Thymine Acts Against The Huckel 4n 2 Rule The Effect Of Metal Ions And H Bond Complexations On The Electronic Structure Of Thymine Organic Biomolecular Chemistry Rsc Publishing

15 3 Aromaticity And The Huckel 4n 2 Rule Chemistry Libretexts Aromaticity Covalent Bond
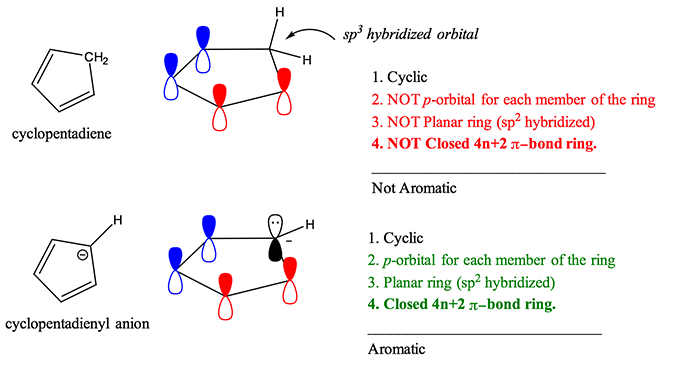
Aromaticity Rules And Definition Organic Chemistry Help
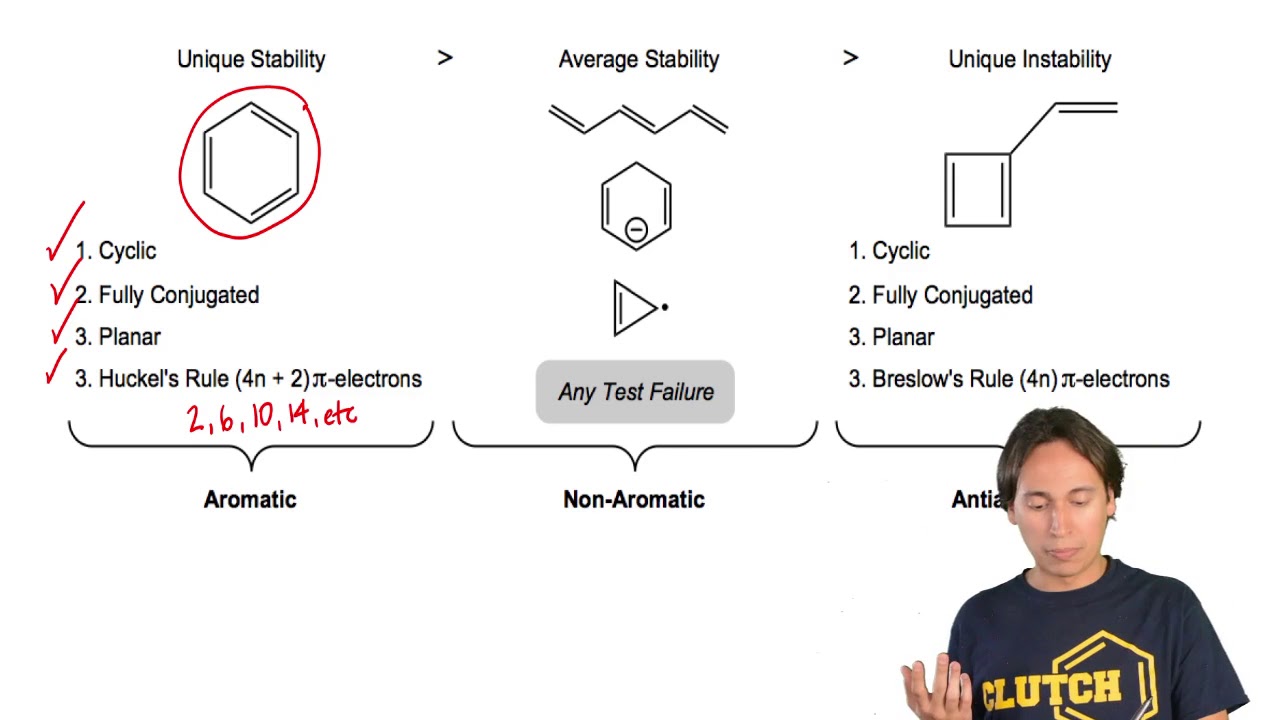
Huckel S Rule Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep

Huckel S Rule For Aromaticity Time Saving Shortcut Youtube

The Criteria For Aromaticity Mcc Organic Chemistry
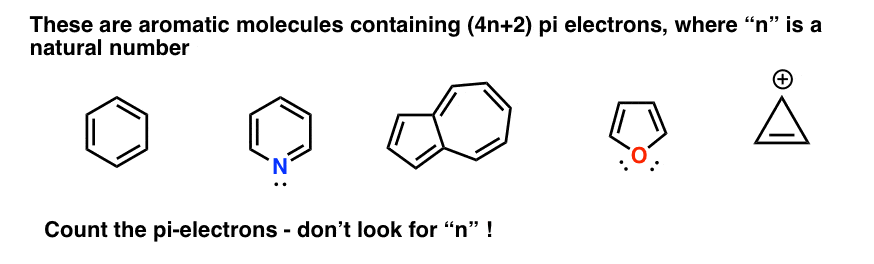
Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry
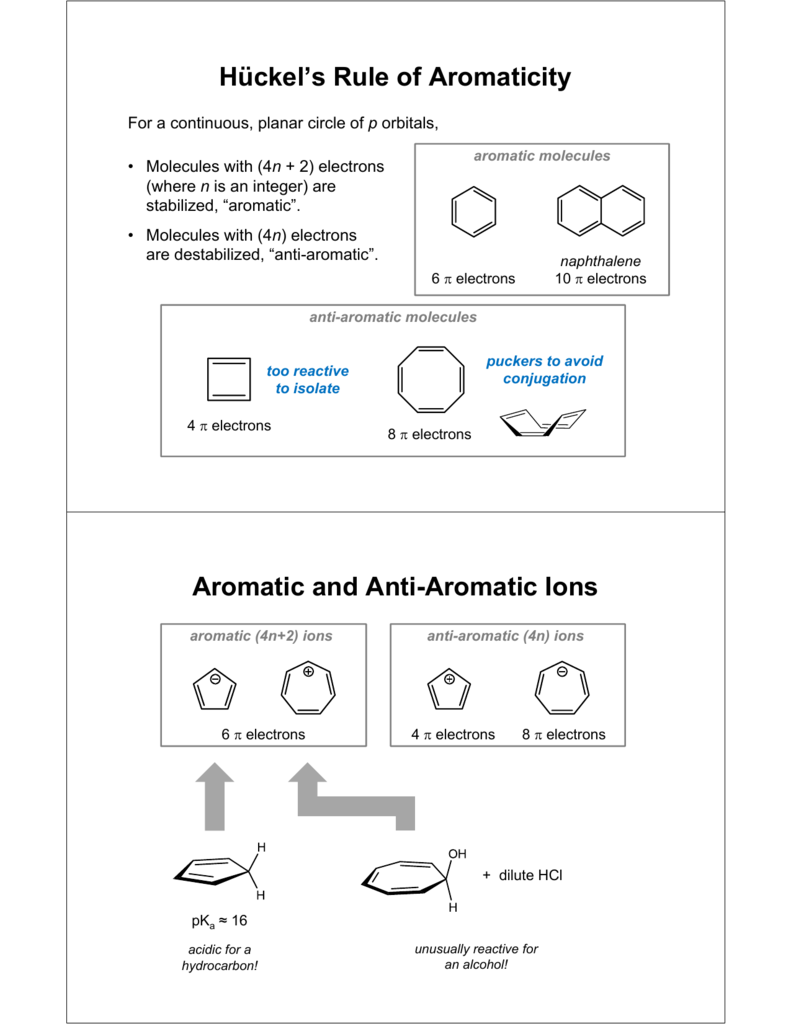
Huckel S Rule Of Aromaticity Aromatic And Anti
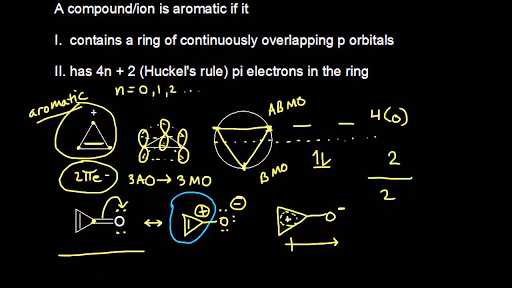
Aromatic Stability Iii Video Khan Academy
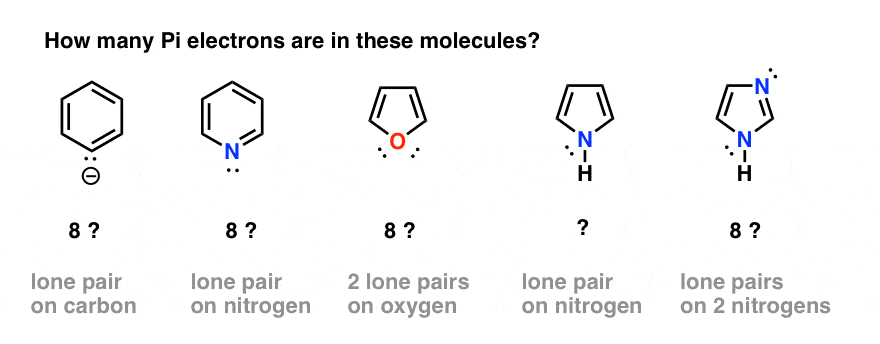
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
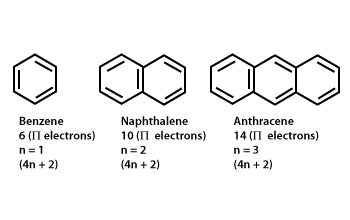
Aromaticity
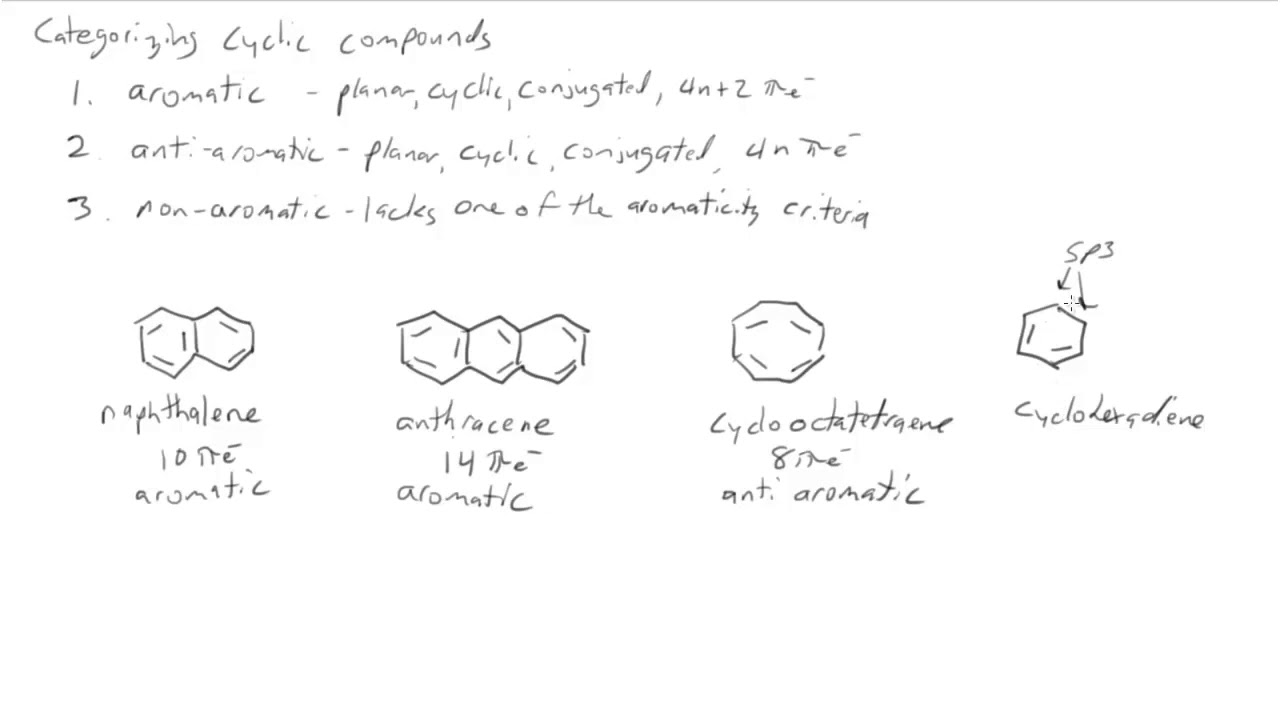
13 7 The Criteria For Aromaticity Huckel S Rule Chemistry Libretexts
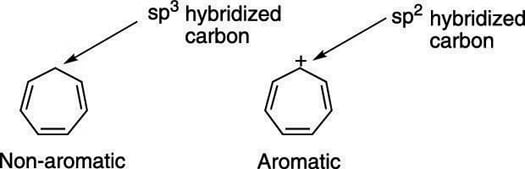
How To Determine The Aromaticity Of A Ring System Dummies

Why Is Cyclopropene Non Aromatic Quora
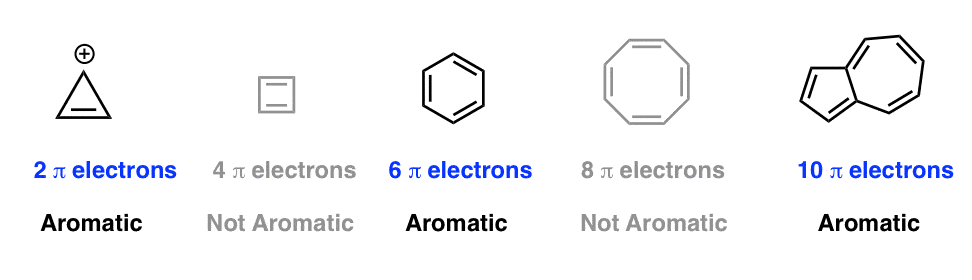
Huckel S Rule What Does 4n 2 Mean Master Organic Chemistry

Indicate Whether Or Not Each Of The Following Structures Is Considered To Be Aromatic Homeworklib
Pericyclic Reaction Selection Rules
2
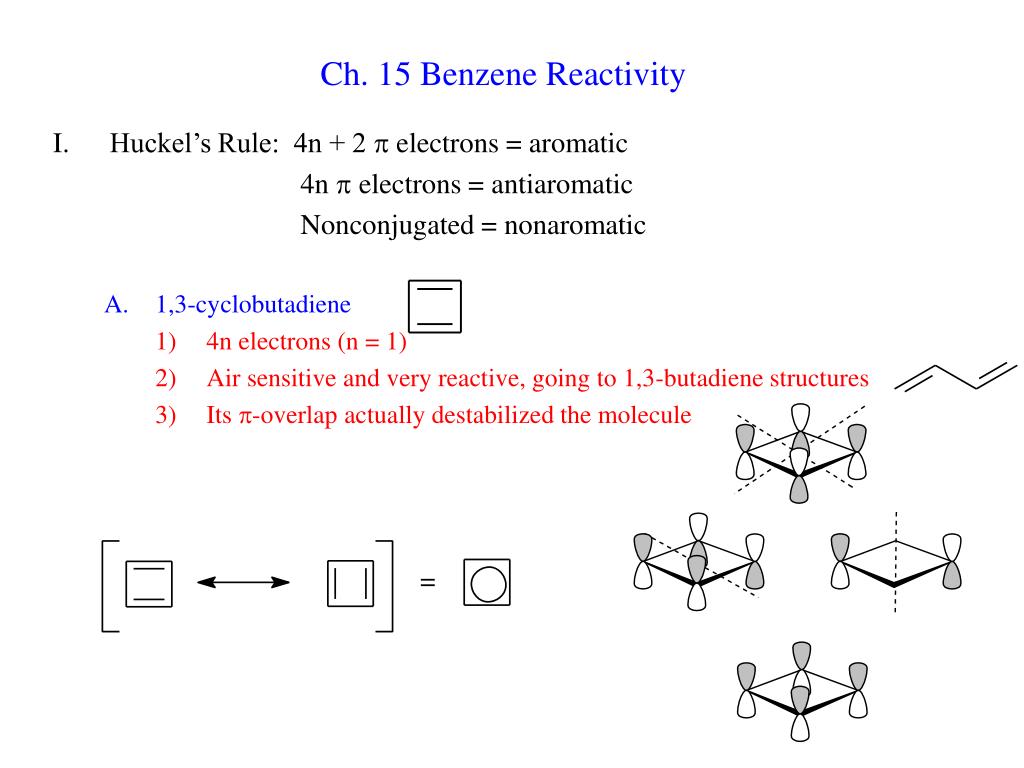
Ppt Ch 15 Benzene Reactivity Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
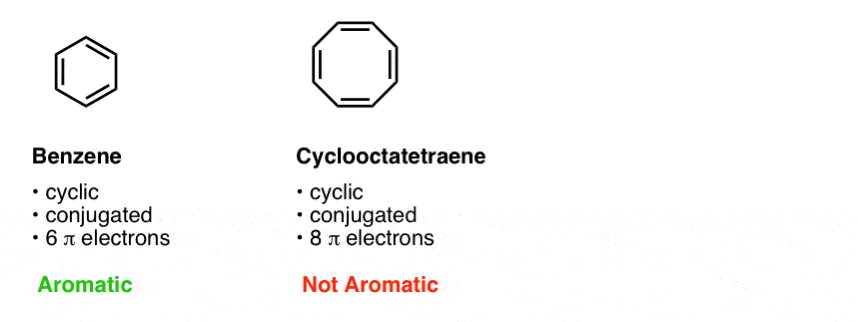
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
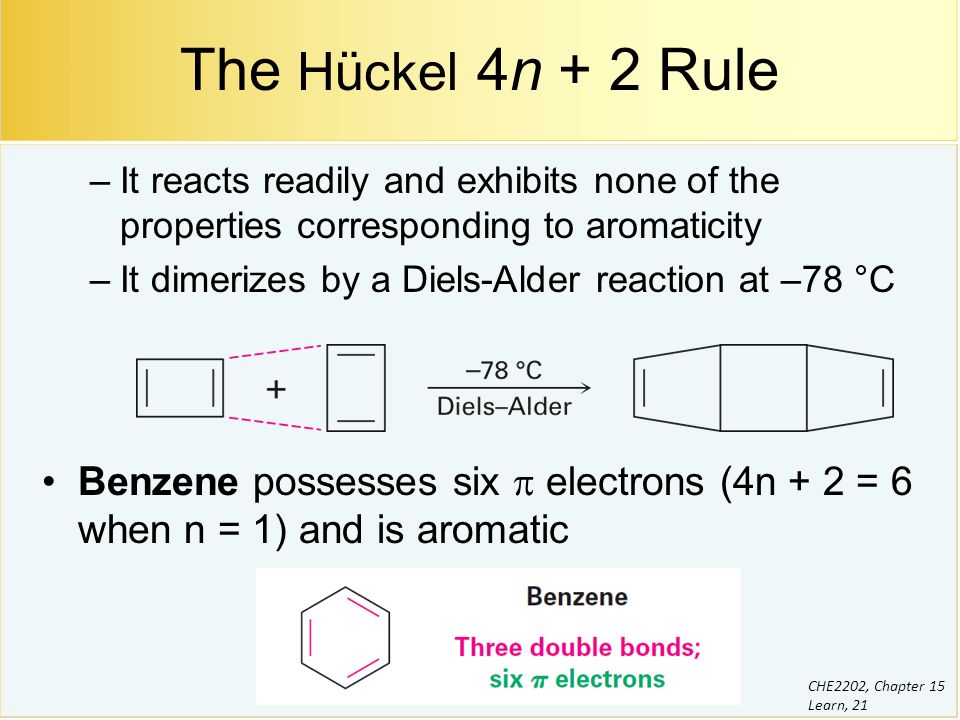
Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download
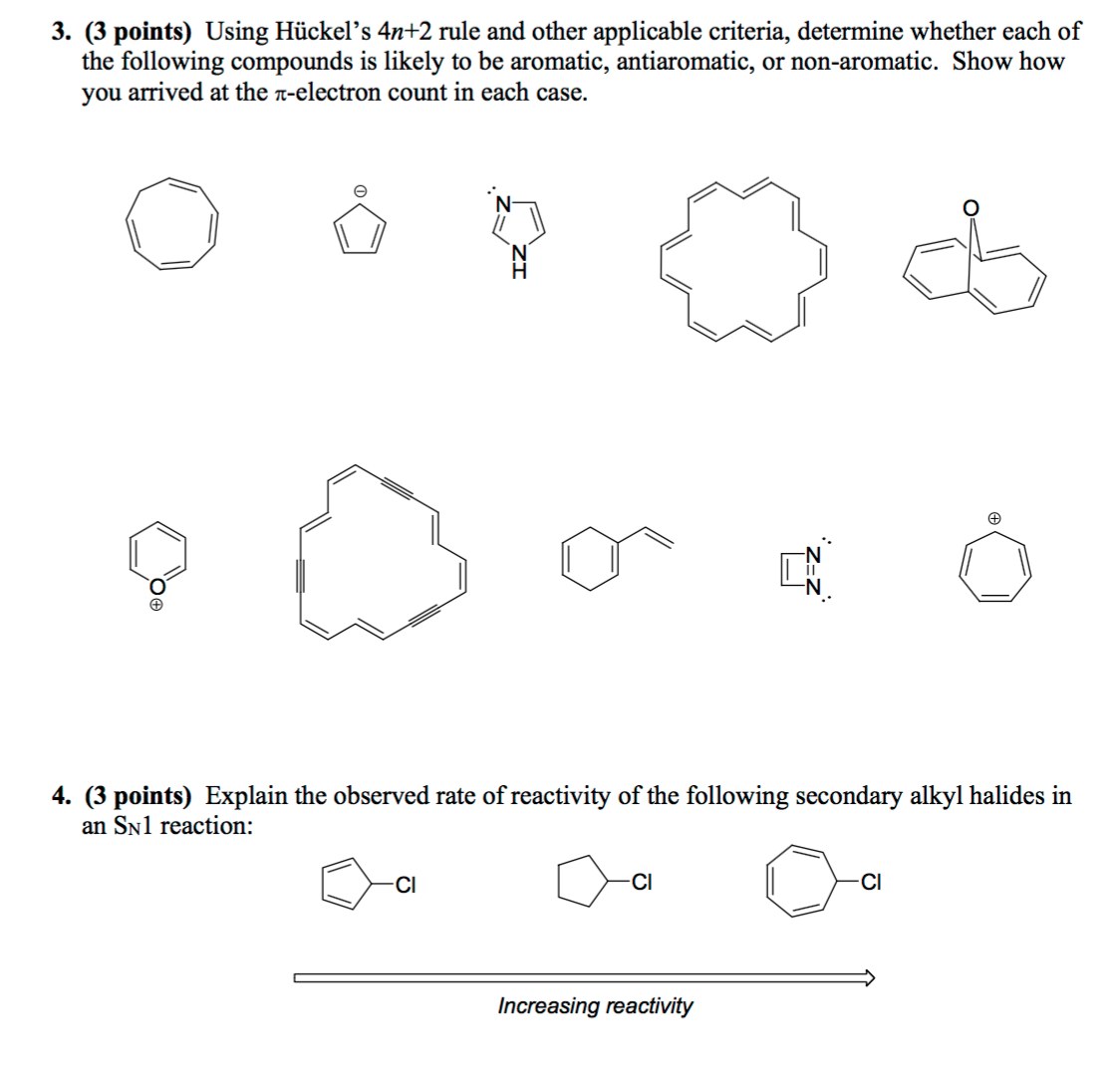
Solved Using Hu Ckel S 4n 2 Rule And Other Applicable Cri Chegg Com

Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Huckel S Rule 4n 2 Heterocycles Aromaticity Youtube

Aromatic Antiaromatic Or Nonaromatic Compounds Chemistry Steps

Aromaticity Tutorial For Cyclic Charged And Heterocyclic Aromatic Compounds

Huckel S Rule Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep
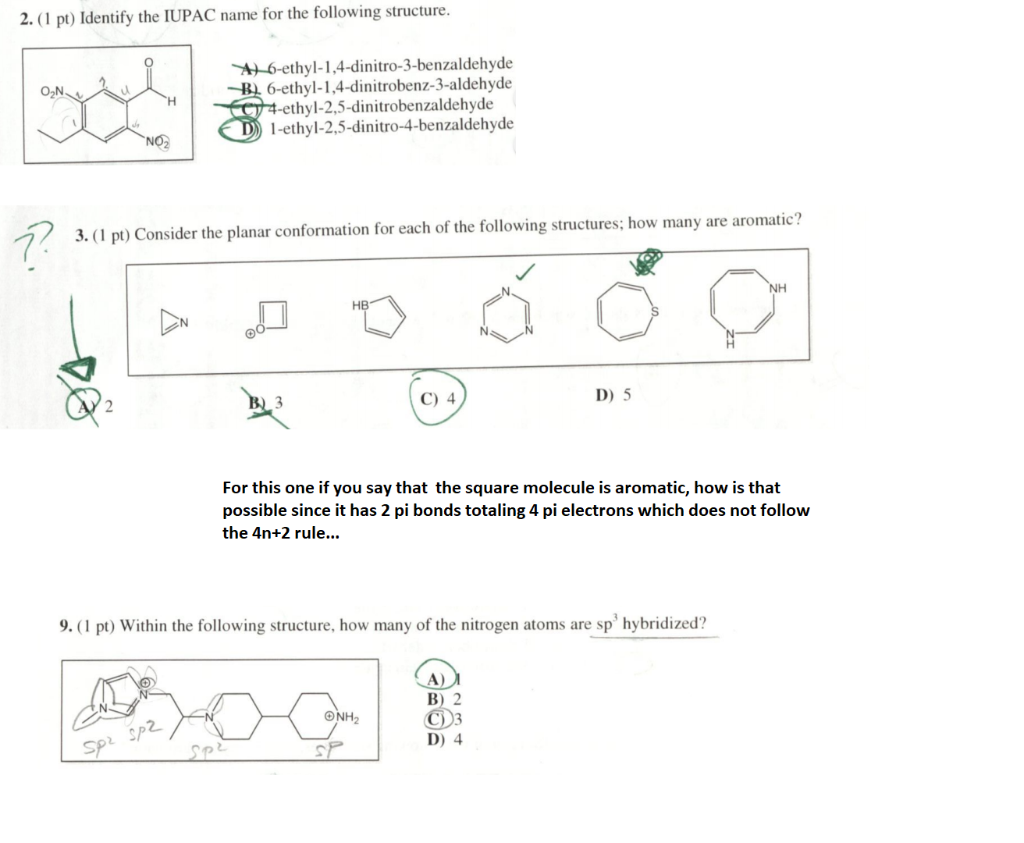
Solved Please Help Me Solve These 3 Questions Also For Chegg Com
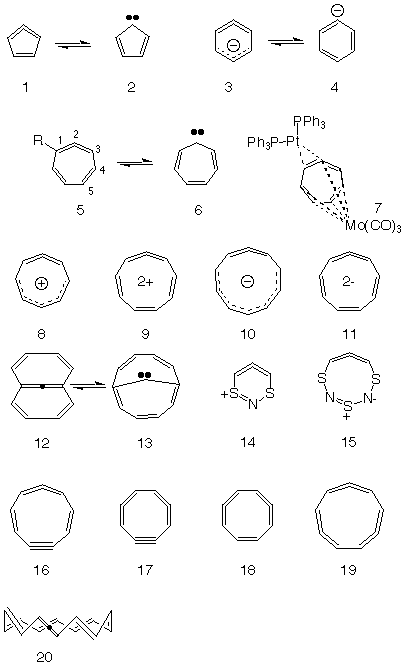
Mobius Aromatics Arising From A C C C Ring Component
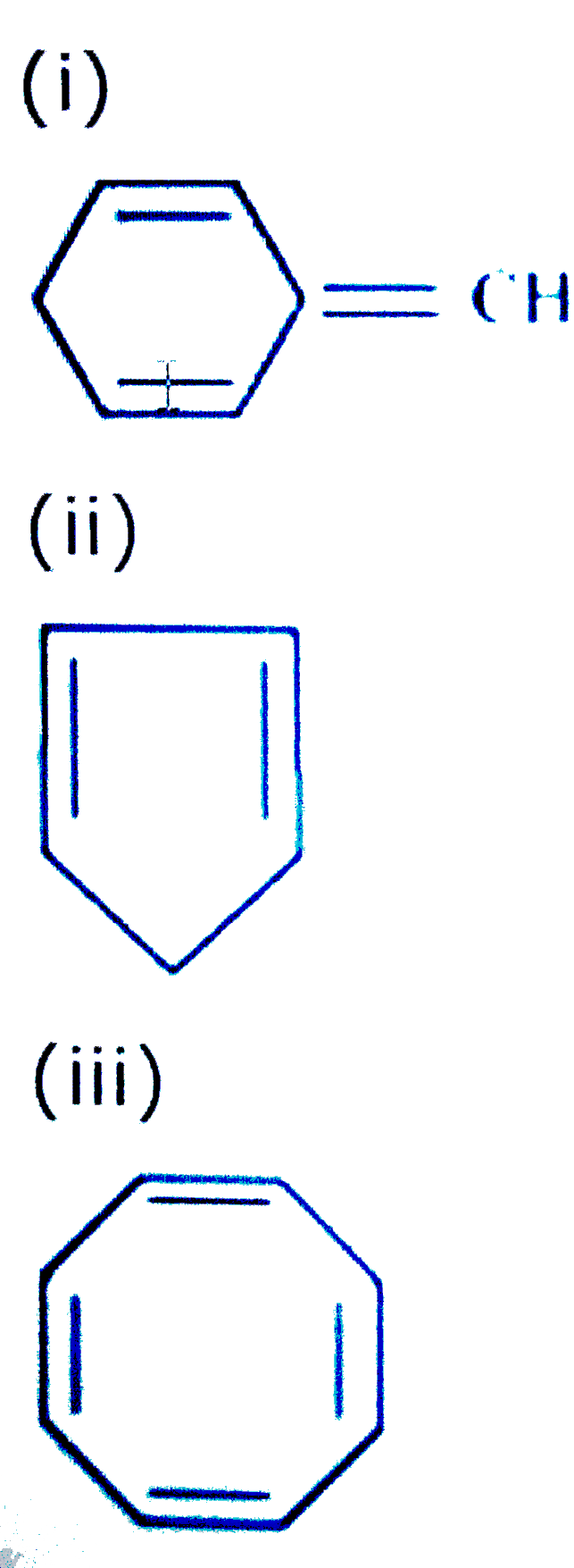
Explain Why The Following Systems Are Not Aromatic Img Src Http
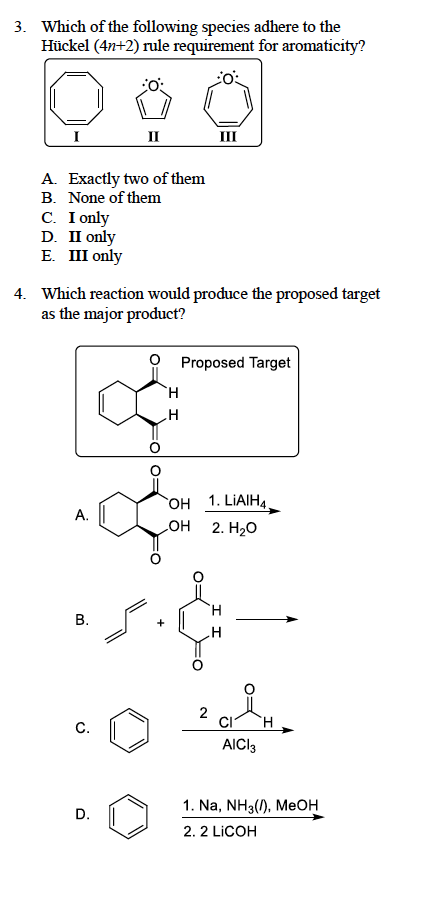
Solved 3 Which Of The Following Species Adhere To The Hu Chegg Com

Solved What Is The Meaning Of N In 4n 2 Aromaticity R Chegg Com
Organic Chemistry On Line
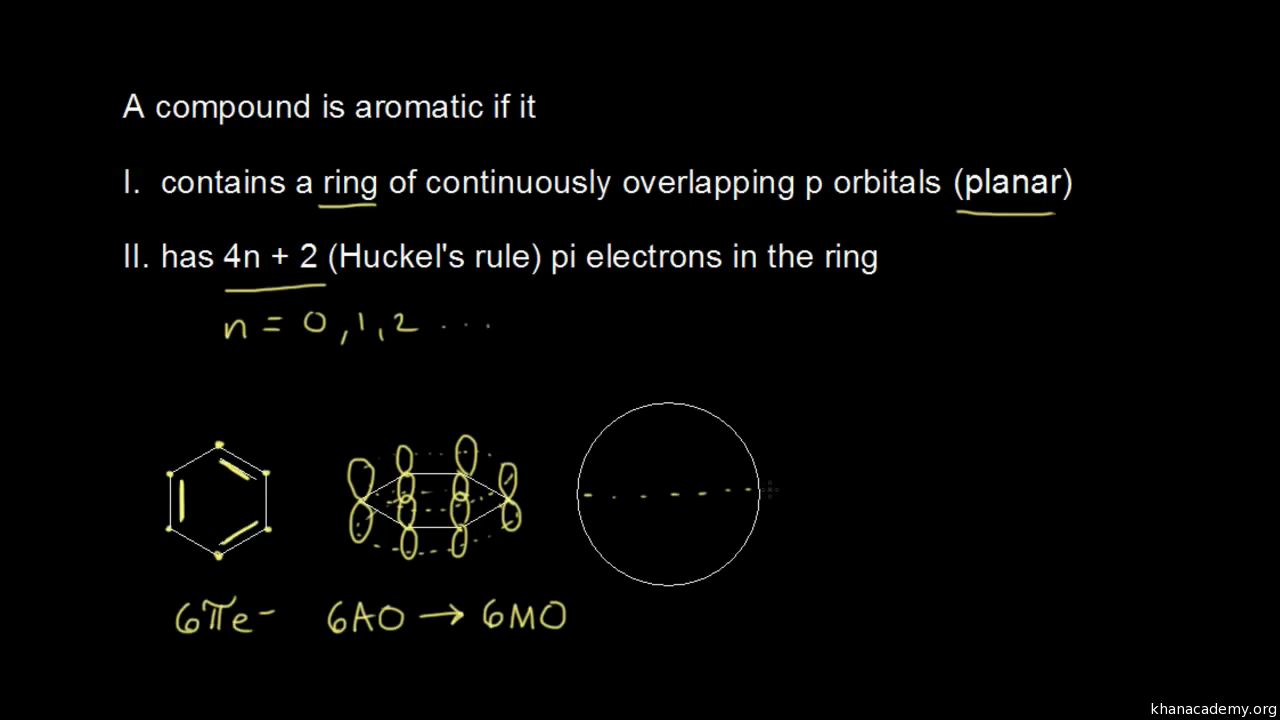
Aromatic Stability I Video Khan Academy
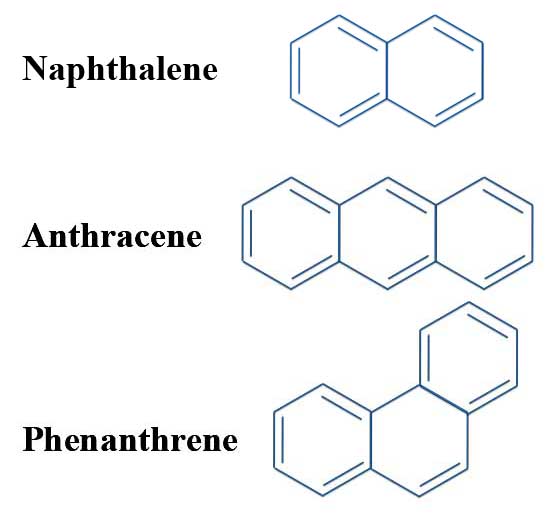
The Problem With Pyrene Michael J S Dewar To The Rescue
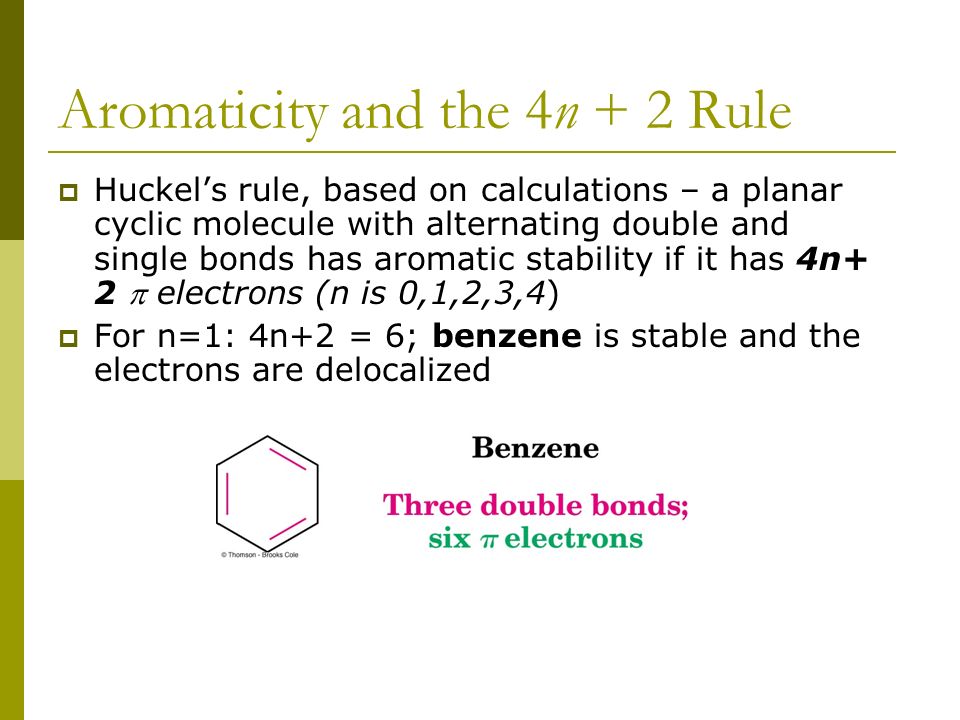
15 Benzene And Aromaticity Ppt Video Online Download
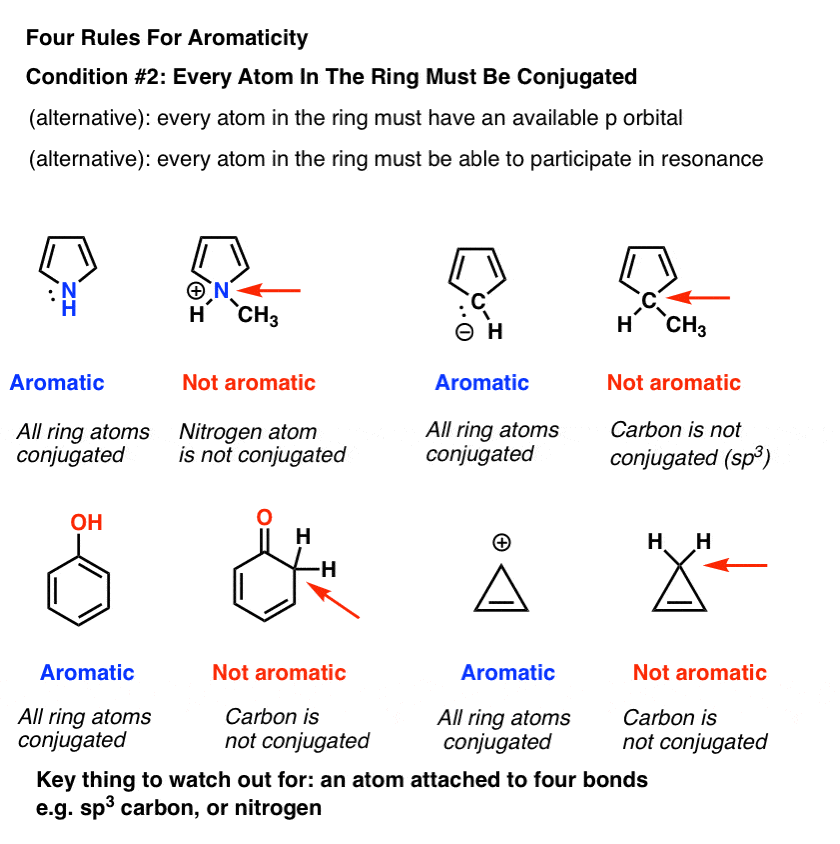
Rules For Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsd3ah2vdmhe7uydhdx6apoxlogkcmi2fl06j52sg1i2jna0doq Usqp Cau
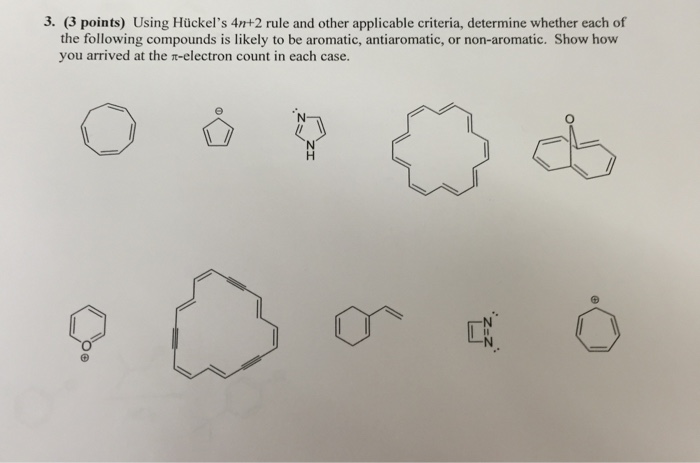
Solved Using Huckel S 4n 2 Rule And Other Applicable Cr Chegg Com

Huckel S Molecular Orbital Theory Huckel S Rule Extended Huckel

Solved Why Isn T The Following Molecule Aromatic Select Chegg Com
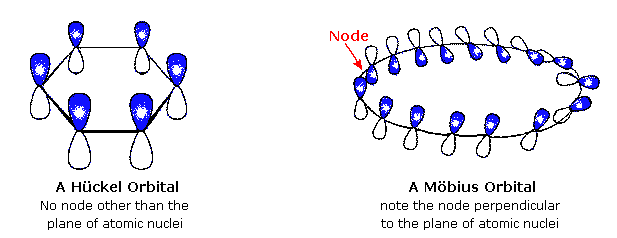
A Mobius 16 Pi Electron System
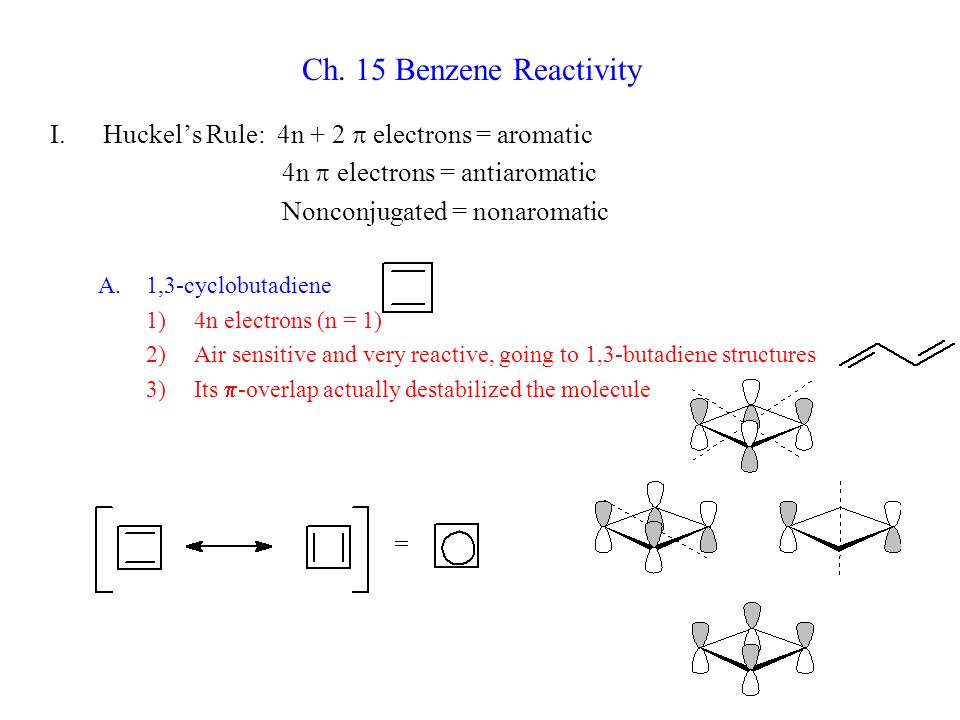
Ch 15 Benzene Reactivity Huckel S Rule 4n 2 P Electrons Aromatic Ppt Video Online Download



